Trends and costs of stereotactic body radiation therapy in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35928617
- PMCID: PMC9344414
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-21-1835
Trends and costs of stereotactic body radiation therapy in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to describe stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) use, outcomes, hospitalizations and costs compared to patients receiving chemotherapy among patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
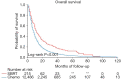
Methods: Using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, we identified patients aged ≥66 with metastatic NSCLC treated with SBRT as first-line treatment between 2004 and 2014. Multivariable logistic regression identified covariates associated with SBRT. Overall survival (OS) between SBRT and chemotherapy was compared using the Kaplan-Meier estimator and Cox proportional hazards regression. To compare hospitalizations and associated costs, we matched patients treated with SBRT to those with comparable prognostic factors receiving chemotherapy.
Results: We identified 215 patients with metastatic NSCLC who received SBRT and 12,486 patients who received chemotherapy as first-line treatment. SBRT use increased from 0.5% to 3% and was associated with older age, female sex, poor disability status, and lower T- and N-stage. OS increased with SBRT, female sex, higher income and decreased with higher Charlson Comorbidity Score ≥2, poor disability status, higher T-stage and higher N-stage. Among a matched sample, SBRT patients underwent fewer hospitalizations vs. chemotherapy patients (73% vs. 81%, P=0.02). Among those hospitalized, SBRT patients incurred higher hospitalization costs ($33,063 vs. $23,865, P<0.001) but costs per month of survival were similar.
Conclusions: SBRT is increasing among Medicare patients with metastatic NSCLC. Our findings suggest that SBRT may play a role in management of select metastatic NSCLC patients in addition to standard-of-care chemotherapy.
Keywords: Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT); Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-Medicare (SEER-Medicare); costs; hospitalizations; metastatic lung cancer.
2022 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-21-1835/coif). All authors report that this work was supported by a Lake Champlain Cancer Research Organization Pilot Grant. Payments were made to the University of Vermont. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources