Research studies on screening tests
- PMID: 35928637
- PMCID: PMC9345258
- DOI: 10.4103/picr.picr_111_22
Research studies on screening tests
Abstract
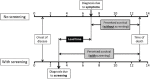
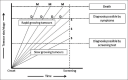
Screening tests are done to diagnose asymptomatic disease in apparently healthy people with the aim to reduce mortality and morbidity from the disease. Certain criteria need to be fulfilled before we adopt population-level screening for any disease. Several biases exist in evaluating screening studies, and the ideal study design would be a randomized trial with hard endpoints such as mortality and morbidity.
Keywords: Diagnosis; mass screening; research methodology.
Copyright: © 2022 Perspectives in Clinical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
No. 385-Indications for Pelvic Examination.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2019 Aug;41(8):1221-1234. doi: 10.1016/j.jogc.2018.12.007. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2019. PMID: 31331610
-
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer: diagnostic strategies and their implications.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 May;(150):1-180. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 17764220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fecal occult blood test for colorectal cancer screening: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(10):1-40. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074514 Free PMC article.
-
Perception, paradox, paradigm: Alice in the wonderland of lung cancer prevention and early detection.Cancer. 2000 Dec 1;89(11 Suppl):2422-31. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20001201)89:11+<2422::aid-cncr16>3.3.co;2-5. Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11147620 Review.
-
Screening mammography for women aged 40 to 49 years at average risk for breast cancer: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2007;7(1):1-32. Epub 2007 Jan 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2007. PMID: 23074501 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Non-Mass Enhancement on MRI 10 Years Before Mammographic Microcalcifications.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2025 May 1;16(3):105-112. doi: 10.6004/jadpro.2025.16.3.3. eCollection 2025 May. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40584011 Free PMC article.
-
Literature- and Experience-Based Consensus for Acute Post-operative Endophthalmitis and Endogenous Endophthalmitis in Taiwan.Ophthalmol Ther. 2024 Jan;13(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00835-5. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Ophthalmol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37934385 Free PMC article.
-
Letter regarding "Value of repeated health screening in 259 apparently healthy mature adult and senior cats followed for 2 years".J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Jan-Feb;39(1):e17271. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17271. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39670719 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilson J, Junger G. Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1968. [Last accessed on 2022 Apr 27]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/37650/WHO_PHP_34.pdf ?s... .
-
- Increase Effectiveness, Maximize Benefits and Minimize Harm. Copenhagen: : WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2020. [Last accessed on 2022 Apr 27]. Screening Programmes: A Short Guide. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/330829/9789289054782-en... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
