Risk Prediction of Injury Among Recreational Badminton Players in India
- PMID: 35928670
- PMCID: PMC9283613
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-022-00663-y
Risk Prediction of Injury Among Recreational Badminton Players in India
Abstract
Background/purpose: Since badminton has emerged as a frequently played non-contact recreational sport in India, it is essential to document the injury patterns and incidence. However, there is no existing literature on this topic among Indian players.
Materials and methods: A web-based questionnaire was circulated among recreational badminton players across North India, enquiring about demographic details, injury characteristics, and factors associated with an injury like BMI, warm-up practice, and physical training.
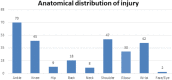
Results: Data of 237 eligible participants revealed an injury incidence rate of 57.1%. The ankle and dominant-side shoulder were the most common anatomical regions affected. The most common injury types were ligament sprain and muscle/tendon strain. Factors like age, frequency, duration of play, type of footwear, BMI, prior warm-up, court surface, and physical training were significantly associated with injury incidence on univariate logistic regression analysis. On multivariate logistic regression analysis, we found male gender, a lack of prior warm-up, inadequate physical training, and age group between 26 and 30 years to be four independent risk factors for injury.
Conclusion: The recreational badminton player of India had a relatively higher incidence of injury compared with the limited published data from other countries. Modifiable factors like a proper warm-up before the game, regular physical fitness training, and injury awareness programs can reduce the injury rates.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s43465-022-00663-y.
Keywords: Badminton; Physical training; Racquet sports; Recreational players; Sports injury; Warm-up.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources