A Phosphoproteomics Study of the Soybean root necrosis 1 Mutant Revealed Type II Metacaspases Involved in Cell Death Pathway
- PMID: 35928708
- PMCID: PMC9344878
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.882561
A Phosphoproteomics Study of the Soybean root necrosis 1 Mutant Revealed Type II Metacaspases Involved in Cell Death Pathway
Abstract
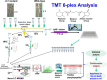
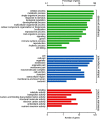
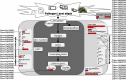
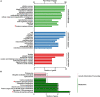
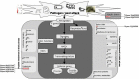
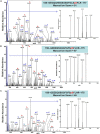
The soybean root necrosis 1 (rn1) mutation causes progressive browning of the roots soon after germination and provides increased tolerance to the soil-borne oomycete pathogen Phytophthora sojae in soybean. Toward understanding the molecular basis of the rn1 mutant phenotypes, we conducted tandem mass tag (TMT)-labeling proteomics and phosphoproteomics analyses of the root tissues of the rn1 mutant and progenitor T322 line to identify potential proteins involved in manifestation of the mutant phenotype. We identified 3,160 proteins. When the p-value was set at ≤0.05 and the fold change of protein accumulation between rn1 and T322 at ≥1.5 or ≤0.67, we detected 118 proteins that showed increased levels and 32 proteins decreased levels in rn1 as compared to that in T322. The differentially accumulated proteins (DAPs) are involved in several pathways including cellular processes for processing environmental and genetic information, metabolism and organismal systems. Five pathogenesis-related proteins were accumulated to higher levels in the mutant as compared to that in T322. Several of the DAPs are involved in hormone signaling, redox reaction, signal transduction, and cell wall modification processes activated in plant-pathogen interactions. The phosphoproteomics analysis identified 22 phosphopeptides, the levels of phosphorylation of which were significantly different between rn1 and T322 lines. The phosphorylation levels of two type II metacaspases were reduced in rn1 as compared to T322. Type II metacaspase has been shown to be a negative regulator of hypersensitive cell death. In absence of the functional Rn1 protein, two type II metacaspases exhibited reduced phosphorylation levels and failed to show negative regulatory cell death function in the soybean rn1 mutant. We hypothesize that Rn1 directly or indirectly phosphorylates type II metacaspases to negatively regulate the cell death process in soybean roots.
Keywords: cell death; metacaspases; phosphoproteomics; proteomics; root necrosis; soybean.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Das, Pal, Bhawal, Zhang and Bhattacharyya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Programmed cell death in the root cortex of soybean root necrosis mutants.Plant J. 1997 Apr;11(4):729-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1997.11040729.x. Plant J. 1997. PMID: 9161033
-
Using single cell type proteomics to identify Al-induced proteomes in outer layer cells and interior tissues in the apical meristem/cell division regions of tomato root-tips.J Proteomics. 2022 Mar 20;255:104486. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2022.104486. Epub 2022 Jan 20. J Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35066208
-
Allelism and molecular mapping of soybean necrotic root mutants.Genome. 2008 Apr;51(4):243-50. doi: 10.1139/G08-001. Genome. 2008. PMID: 18356960
-
Evolutionary Diversity and Function of Metacaspases in Plants: Similar to but Not Caspases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4588. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094588. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caspases in plants: metacaspase gene family in plant stress responses.Funct Integr Genomics. 2015 Nov;15(6):639-49. doi: 10.1007/s10142-015-0459-7. Epub 2015 Aug 16. Funct Integr Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26277721 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond the trinity: unraveling a fourth clade in the PEBP gene family in plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 May 18;44(6):122. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03505-x. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40383720
References
-
- Ahmad R., Zuily-Fodil Y., Passaquet C., Bethenod O., Roche R., Repellin A. (2012). Ozone and aging up-regulate type II metacaspase gene expression and global metacaspase activity in the leaves of field-grown maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Chemosphere 87 789–795. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.081 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baskett J. A. (2012). A Type II Metacaspase Interacts with Rps1-k-2 in Soybean and Analysis of the Soybean Metacaspase Gene Family. M.S. thesis. Ames, IA: Iowa State University.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

