Exosomes with FOXP3 from gene-modified dendritic cells ameliorate the development of EAE by regulating the balance of Th/Treg
- PMID: 35928722
- PMCID: PMC9346388
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.72655
Exosomes with FOXP3 from gene-modified dendritic cells ameliorate the development of EAE by regulating the balance of Th/Treg
Abstract
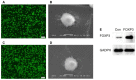
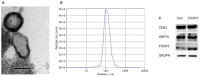
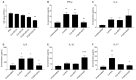
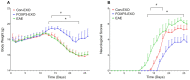
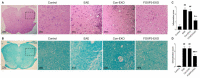
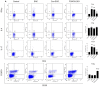
Objective: To investigate the efficiency and potential mechanisms of exosomes from dendritic cells (DCs) transfected with Forkhead box protein P3 (FOXP3) in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Method: Mouse bone marrow-derived immature DCs were loaded with adenovirus carrying FOXP3 gene, and exosomes were generated. Then the exosomes with FOXP3 (FOXP3-EXOs) were co-cultured with CD4+T cell in vitro to evaluate their potential on CD4+T cell proliferation and differentiation, and injected into EAE mice to assess their effects on the development of EAE. Result: FOXP3-EXOs were effective to inhibit the CD4+T cell proliferation and the production of Interferon gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-17, while they promoted the production of IL-10 in vitro. Moreover, FOXP3-EXOs treatment significantly decreased the neurological scores, reduced the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the spinal cord, and decreased demyelination in comparison to saline and Con-EXOs treated EAE mice. Moreover, the FOXP3-EXOs treatment resulted in obvious increases in the levels of regulatory T (Treg) cells and IL-10, whereas levels of T helper 1 (Th1) cells, Th17 cells, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-17 decreased significantly in the splenocyte culture of EAE mice. Conclusion: The present study preliminarily investigated the effects and potential mechanisms of FOXP3-EXOs in EAE and revealed that the FOXP3-EXOs could inhibit the production of Th1 and Th17 cells and promote the production of Treg cells as well as ameliorate the development of EAE. The neuroprotective effects of FOXP3-EXOs on EAE are likely due to the regulation of Th/Treg balance.
Keywords: FOXP3; Multiple sclerosis; dendritic cell; exosomes; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomes with membrane-associated TGF-β1 from gene-modified dendritic cells inhibit murine EAE independently of MHC restriction.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Sep;43(9):2461-72. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243295. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23716181
-
S3I-201, a selective stat3 inhibitor, ameliorates clinical symptoms in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through the regulation of multiple intracellular signalling in Th1, Th17, and treg cells.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 May;73:104658. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.104658. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36989705
-
[Therapeutic Effect of SPK1 Gene Transfected Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice and Its Effect on T Helper Cell 17/Regulatory T Cells Balance].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020 Dec 30;42(6):755-765. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11888. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33423722 Chinese.
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+ T-Cell Plasticity in Non-Infectious Retinal Inflammatory Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 3;22(17):9584. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179584. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Possible Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Interventions of Immune-Mediated Central Demyelinating Diseases.Exp Neurobiol. 2024 Apr 30;33(2):47-67. doi: 10.5607/en24002. Exp Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38724476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of dendritic cell‑derived exosomes in allergic rhinitis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Dec;52(6):117. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5320. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37888754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Exosomes as the Next-Generation Bio-Shuttles: The Next Biggest Approach against Th17 Cell Catastrophe.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7647. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087647. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Dendritic Cells Exhibit Protective and Therapeutic Potential Against Chemically Induced Chronic Pancreatitis in Rats.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1728-1744. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02150-y. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39424751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Semin Neurol. 2016;36:115–27. - PubMed
-
- Stampanoni Bassi M, Iezzi E, Centonze D. Multiple sclerosis: Inflammation, autoimmunity and plasticity. Handb Clin Neurol. 2022;184:457–70. - PubMed
-
- Olsson T, Barcellos LF, Alfredsson L. Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13:25–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

