Machine learning-based combined nomogram for predicting the risk of pulmonary invasive fungal infection in severely immunocompromised patients
- PMID: 35928747
- PMCID: PMC9347049
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-4980
Machine learning-based combined nomogram for predicting the risk of pulmonary invasive fungal infection in severely immunocompromised patients
Abstract
Background: Early and accurate diagnosis of invasive fungal infection (IFI) is pivotal for the initiation of effective antifungal therapy for patients with hematologic malignancies.
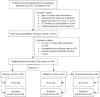
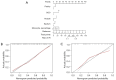
Methods: This retrospective study involved 235 patients with hematologic malignancies and pulmonary infections diagnosed as IFIs (n=118) or bacterial pneumonia (n=117). Patients were randomly divided into training (n=188) and validation (n=47) datasets. Four feature selection methods with nine classifiers were implemented to select the optimal machine learning (ML) model using five-fold cross-validation. A radiomic signature was constructed using a linear ML algorithm, and a radiomic score (Radscore) was calculated. The combined model was developed with the Radscore, the significant clinical and radiologic factors were selected using multivariable logistic regression, and the results were presented as a clinical radiomic nomogram. A prospective pilot study was also conducted to compare the classification performance of the combined nomogram with practicing radiologists.
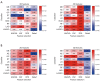
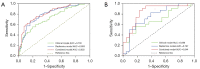
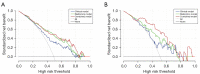
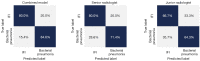
Results: Significant differences were found in the Radscore between IFI and bacterial pneumonia patients in the training (0.683 vs. -0.724, P<0.001) and validation set (0.353 vs. -0.717, P=0.002). The combined model showed good discrimination performance in the validation cohort [area under the curve (AUC) =0.844] and outperformed the clinical (AUC =0.696) and radiomics (AUC =0.767) model alone (both P<0.05).
Conclusions: The clinical radiomic nomogram can serve as a promising predictive tool for IFI in patients with hematologic malignancies.
Keywords: Machine learning (ML); computed tomography (CT); hematologic malignancy; invasive fungal infection (IFI); radiomics.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-21-4980/coif). TZ and HL have associations with Philips Healthcare, and each provided technical support for data analysis. HCW owns (minority) shares in Oncoradiomics. PL reports, within and outside the submitted work, grants/sponsored research agreements from Varian Medical, Oncoradiomics, ptTheragnostic, Health Innovation Ventures, and DualTpharma. He received an advisor/presenter fee and/or reimbursement of travel costs/external grant writing fee and/or in-kind manpower contribution from Oncoradiomics, BHV, Merck, and Convert Pharmaceuticals. He owns shares in Oncoradiomics SA and Convert Pharmaceuticals SA. He is a coinventor of 2 issued patents with royalties on radiomics (PCT/NL2014/050248, PCT/NL2014/050728) licensed to Oncoradiomics, 1 issued patent on mtDNA (PCT/EP2014/059089) licensed to ptTheragnostic/DNAmito, and 3 nonpatentable inventions (software) licensed to ptTheragnostic/DNAmito, Oncoradiomics, and Health Innovation Ventures. None of the authors had control of the data in a manner that would present a conflict of interest for the other employees or consultant authors. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Clinical-Radiomic Nomogram Based on Unenhanced Computed Tomography for Predicting the Risk of Aldosterone-Producing Adenoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 9;11:634879. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.634879. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34307119 Free PMC article.
-
A Nomogram Combined Radiomic and Semantic Features as Imaging Biomarker for Classification of Ovarian Cystadenomas.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 1;10:895. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00895. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32547958 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative diagnosis of malignant pulmonary nodules in lung cancer screening with a radiomics nomogram.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Jan;40(1):16-24. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12002. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32125097 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Phase CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Discrimination Between Pancreatic Serous Cystic Neoplasm From Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 1;11:699812. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699812. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34926238 Free PMC article.
-
A CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram to Predict Complete Ablation of Pulmonary Malignancy: A Multicenter Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 10;12:841678. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.841678. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35223526 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A CT-based nomogram for differentiating invasive fungal disease of the lung from bacterial pneumonia.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Oct 3;22(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00903-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36184590 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging innovative diagnostics as a tool to contain superbugs.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Mar 26;118(4):63. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02075-y. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40140116 Review.
-
Development and validation of a machine learning-based nomogram for survival prediction of patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma after curative-intent resection.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 12;15(1):25220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10329-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40652016 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-based intratumoral and peritumoral machine learning ultrasomics model for predicting the pathological grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jan 18;25(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01555-x. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39827128 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a clinic machine-learning nomogram for the prediction of risk stratifications of prostate cancer based on functional subsets of peripheral lymphocyte.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 12;21(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04318-w. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37438820 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
