Anti-C1q autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus patients enhance CD40-CD154-mediated inflammation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro
- PMID: 35928801
- PMCID: PMC9345742
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1408
Anti-C1q autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus patients enhance CD40-CD154-mediated inflammation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro
Abstract
Objectives: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a clinically heterogeneous autoimmune disease with complex pathogenic mechanisms. Complement C1q has been shown to play a major role in SLE, and autoantibodies against C1q (anti-C1q) are strongly associated with SLE disease activity and severe lupus nephritis suggesting a pathogenic role for anti-C1q. Whereas C1q alone has anti-inflammatory effects on human monocytes and macrophages, C1q/anti-C1q complexes favor a pro-inflammatory phenotype. This study aimed to elucidate the inflammatory effects of anti-C1q on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
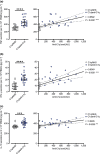
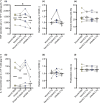
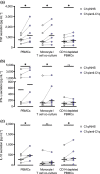
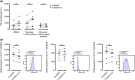
Methods: Isolated monocytes, isolated T cells and bulk PBMCs of healthy donors with or without concomitant T cell activation were exposed to C1q or complexes of C1q and SLE patient-derived anti-C1q (C1q/anti-C1q). Functional consequences of C1q/anti-C1q on cells were assessed by determining cytokine secretion, monocyte surface marker expression, T cell activation and proliferation.
Results: Exposure of isolated T cells to C1q or C1q/anti-C1q did not affect their activation and proliferation. However, unspecific T cell activation in PBMCs in the presence of C1q/anti-C1q resulted in increased TNF, IFN-γ and IL-10 secretion compared with C1q alone. Co-culture and inhibition experiments showed that the inflammatory effect of C1q/anti-C1q on PBMCs was due to a direct CD40-CD154 interaction between activated T cells and C1q/anti-C1q-primed monocytes. The CD40-mediated inflammatory reaction of monocytes involves TRAF6 and JAK3-STAT5 signalling.
Conclusion: In conclusion, C1q/anti-C1q have a pro-inflammatory effect on monocytes that depends on T cell activation and CD40-CD154 signalling. This signalling pathway could serve as a therapeutic target for anti-C1q-mediated inflammation.
Keywords: C1q; CD40; T cells; anti‐C1q autoantibodies; monocytes; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yaniv G, Twig G, Shor DB‐A et al. A volcanic explosion of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a diversity of 180 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Autoimmun Rev 2015; 14: 75–79. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann M, Voll RE, Zoller OM, Hagenhofer M, Ponner BB, Kalden JR. Impaired phagocytosis of apoptotic cell material by monocyte‐derived macrophages from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1998; 41: 1241–1250. - PubMed
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1140–1144. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
