The functions of long noncoding RNAs on regulation of F-box proteins in tumorigenesis and progression
- PMID: 35928868
- PMCID: PMC9343830
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.963617
The functions of long noncoding RNAs on regulation of F-box proteins in tumorigenesis and progression
Abstract
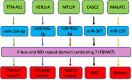
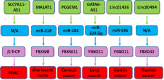
Accumulated evidence has revealed that F-box protein, a subunit of SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, participates in carcinogenesis and tumor progression via targeting its substrates for ubiquitination and degradation. F-box proteins could be regulated by cellular signaling pathways and noncoding RNAs in tumorigenesis. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), one type of noncoding RNAs, has been identified to modulate the expression of F-box proteins and contribute to oncogenesis. In this review, we summarize the role and mechanisms of multiple lncRNAs in regulating F-box proteins in tumorigenesis, including lncRNAs SLC7A11-AS1, MT1JP, TUG1, FER1L4, TTN-AS1, CASC2, MALAT1, TINCR, PCGEM1, linc01436, linc00494, GATA6-AS1, and ODIR1. Moreover, we discuss that targeting these lncRNAs could be helpful for treating cancer via modulating F-box protein expression. We hope our review can stimulate the research on exploration of molecular insight into how F-box proteins are governed in carcinogenesis. Therefore, modulation of lncRNAs is a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer therapy via regulation of F-box proteins.
Keywords: F-box protein; cancer; lncRNAs; noncoding RNA; oncogenesis; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Xia, Chen, Huang, Mei and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of F-box proteins by noncoding RNAs in human cancers.Cancer Lett. 2019 Dec 1;466:61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.008. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31546023 Review.
-
Emerging roles of long noncoding RNAs in chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Aug;83:303-318. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33207266 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs: functions and mechanisms in colon cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Nov 28;19(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01287-2. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33246471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TTN-AS1 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for multiple cancers.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Mar;135:111169. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111169. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33433359 Review.
-
F-box only protein 9 and its role in cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1537-1544. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07057-7. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35025031 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of long noncoding RNA TTN-AS1 in various malignancies.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Oct;6(10):e1876. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1876. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 37528740 Free PMC article.
-
F-box proteins at the crossroads of ubiquitination and tumor immunity: regulatory networks and immunotherapy strategies.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1596344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1596344. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of lncRNA H19 polymorphisms with cancer susceptibility: An updated meta-analysis based on 53 studies.Front Genet. 2022 Dec 14;13:1051766. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1051766. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36588790 Free PMC article.
-
FBXL18 is required for ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration through activating AKT signaling.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):1977-1990. doi: 10.62347/HHXX8166. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883375 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

