von Willebrand Factor: A Central Regulator of Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation Through Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Outward Remodeling
- PMID: 35929448
- PMCID: PMC9496319
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024581
von Willebrand Factor: A Central Regulator of Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation Through Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Outward Remodeling
Abstract
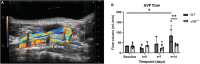
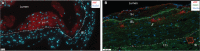
Background Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) maturation failure is a main limitation of vascular access. Maturation is determined by the intricate balance between outward remodeling and intimal hyperplasia, whereby endothelial cell dysfunction, platelet aggregation, and vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation play a crucial role. von Willebrand Factor (vWF) is an endothelial cell-derived protein involved in platelet aggregation and VSMC proliferation. We investigated AVF vascular remodeling in vWF-deficient mice and vWF expression in failed and matured human AVFs. Methods and Results Jugular-carotid AVFs were created in wild-type and vWF-/- mice. AVF flow was determined longitudinally using ultrasonography, whereupon AVFs were harvested 14 days after surgery. VSMCs were isolated from vena cavae to study the effect of vWF on VSMC proliferation. Patient-matched samples of the basilic vein were obtained before brachio-basilic AVF construction and during superficialization or salvage procedure 6 weeks after AVF creation. vWF deficiency reduced VSMC proliferation and macrophage infiltration in the intimal hyperplasia. vWF-/- mice showed reduced outward remodeling (1.5-fold, P=0.002) and intimal hyperplasia (10.2-fold, P<0.0001). AVF flow in wild-type mice was incremental over 2 weeks, whereas flow in vWF-/- mice did not increase, resulting in a two-fold lower flow at 14 days compared with wild-type mice (P=0.016). Outward remodeling in matured patient AVFs coincided with increased local vWF expression in the media of the venous outflow tract. Absence of vWF in the intimal layer correlated with an increase in the intima-media ratio. Conclusions vWF enhances AVF maturation because its positive effect on outward remodeling outweighs its stimulating effect on intimal hyperplasia.
Keywords: AVF maturation; VSMC; intimal hyperplasia; outward remodeling; von Willebrand Factor.
Figures







References
-
- Schmidli J, Widmer MK, Basile C, de Donato G, Gallieni M, Gibbons CP, Haage P, Hamilton G, Hedin U, Kamper L, et al. Vascular access: 2018 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55:757–818. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banerjee T, Kim SJ, Astor B, Shafi T, Coresh J, Powe NR. Vascular access type, inflammatory markers, and mortality in incident hemodialysis patients: the Choices for Healthy Outcomes in Caring for End‐Stage Renal Disease (CHOICE) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:954–961. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.07.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

