Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel understandings and therapeutic strategies based on bile acids (Review)
- PMID: 35929515
- PMCID: PMC9450808
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5407
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel understandings and therapeutic strategies based on bile acids (Review)
Abstract
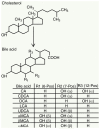
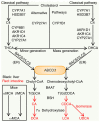
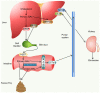
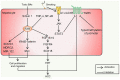
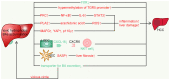
Bile acids (BAs) are the major components of bile and products of cholesterol metabolism. Cholesterol is catalyzed by a variety of enzymes in the liver to form primary BAs, which are excreted into the intestine with bile, and secondary BAs are formed under the modification of the gut microbiota. Most of the BAs return to the liver via the portal vein, completing the process of enterohepatic circulation. BAs have an important role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which may participate in the progression of HCC by recognizing receptors such as farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and mediating multiple downstream pathways. Certain BAs, such as ursodeoxycholic acid and obeticholic acid, were indicated to be able to delay liver injury and HCC progression. In the present review, the structure and function of BAs were introduced and the metabolism of BAs and the process of enterohepatic circulation were outlined. Furthermore, the mechanisms by which BAs participate in the development of HCC were summarized and possible strategies for targeting BAs and key sites of their metabolic processes to treat HCC were suggested.
Keywords: bile acid; enterohepatic circulation; farnesoid x receptor; hepatocellular carcinoma; obeticholic acid; ursodeoxycholic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer. J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Chen K, Li F, Gu Z, Liu Q, He L, Shao T, Song Q, Zhu F, Zhang L, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents liver fibrosis through inhibiting hepatic bile acid synthesis and enhancing bile acid excretion in mice. Hepatology. 2020;71:2050–2066. doi: 10.1002/hep.30975. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
