The uncoating of EV71 in mature late endosomes requires CD-M6PR
- PMID: 35929543
- PMCID: PMC9493940
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.059469
The uncoating of EV71 in mature late endosomes requires CD-M6PR
Abstract
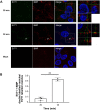
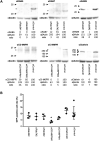
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is one of the causative agents of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, which in some circumstances could lead to severe neurological diseases. Despite of its importance for human health, little is known about the early stages of EV71 infection. EV71 starts uncoating with its receptor, human scavenger receptor B2 (hSCARB2), at low pH. We show that EV71 was not targeted to lysosomes in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells overexpressing hSCARB2 and that the autophagic pathway is not essential for EV71 productive uncoating. Instead, EV71 was efficiently uncoated 30 min after infection in late endosomes (LEs) containing hSCARB2, mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR), RAB9, bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate and lysosomal associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2). Furthering the notion that mature LEs are crucial for EV71 uncoating, cation-dependent (CD)-M6PR knockdown impairs EV71 infection. Since hSCARB2 interacts with cation-independent (CI)-M6PR through M6P-binding sites and CD-M6PR also harbor a M6P-binding site, CD-M6PR is likely to play important roles in EV71 uncoating in LEs.
Keywords: EV71; Late endosomes; Mannose 6-phosphate receptor; SCARB2; Uncoating.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular determinants of enterovirus 71 viral entry: cleft around GLN-172 on VP1 protein interacts with variable region on scavenge receptor B 2.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6406-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.301622. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22219187 Free PMC article.
-
Human SCARB2-mediated entry and endocytosis of EV71.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030507. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22272359 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Murine Model Expressing a Chimeric mSCARB2/hSCARB2 Receptor Is Highly Susceptible to Oral Infection with Clinical Isolates of Enterovirus 71.J Virol. 2019 May 15;93(11):e00183-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00183-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30894476 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of an enterovirus 71 receptor; SCARB2].Uirusu. 2009 Dec;59(2):189-94. doi: 10.2222/jsv.59.189. Uirusu. 2009. PMID: 20218327 Review. Japanese.
-
[Advances in research of SCARB2 functions and related disorders].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;32(5):723-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2015.05.025. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26419000 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of enterovirus VP0 maturation cleavage based on the structure of a stabilised assembly intermediate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 6:2024.04.06.588229. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.06.588229. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 19;20(9):e1012511. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012511. PMID: 38617325 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The host mannose-6-phosphate pathway and viral infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 31;14:1349221. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1349221. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38357444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterovirus-A71 exploits RAB11 to recruit chaperones for virus morphogenesis.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jun 28;31(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01053-2. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38943128 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of enterovirus VP0 maturation cleavage based on the structure of a stabilised assembly intermediate.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 19;20(9):e1012511. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012511. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39298524 Free PMC article.
-
Enterovirus A71 does not meet the uncoating receptor SCARB2 at the cell surface.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Feb 15;20(2):e1012022. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012022. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38359079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanz, J., Groth, J., Zachos, C., Wehling, C., Saftig, P. and Schwake, M. (2010). Disease-causing mutations within the lysosomal integral membrane protein type 2 (LIMP-2) reveal the nature of binding to its ligand beta-glucocerebrosidase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 563-572. 10.1093/hmg/ddp523 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen, P., Song, Z., Qi, Y., Feng, X., Xu, N., Sun, Y., Wu, X., Yao, X., Mao, Q., Li, X.et al. (2012). Molecular determinants of enterovirus 71 viral entry: cleft around GLN-172 on VP1 protein interacts with variable region on scavenge receptor B 2. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 6406-6420. 10.1074/jbc.M111.301622 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

