Comparison of the Outcomes between AO Type B2 Thoracolumbar Fracture with and without Disc Injury after Posterior Surgery
- PMID: 35929591
- PMCID: PMC9483068
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13400
Comparison of the Outcomes between AO Type B2 Thoracolumbar Fracture with and without Disc Injury after Posterior Surgery
Abstract
Objective: The type AO B2 thoracolumbar fracture is a kind of flexion-distraction injury and the effect of disc injury on treatment results of patients with B2 fracture remains unclear. The objective of the current study was to compare and analyze the outcomes in AO Type B2 thoracolumbar fracture patients with and without disc injuries in terms of the Cobb angle of kyphosis, the incidence of complication, and the rate of implant failure.
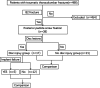
Methods: This is a retrospective study. Of the 486 patients with thoracolumbar fractures who underwent posterior fixation, 38 patients with AO type B2 injuries were included. All the patients were divided into two groups according to changes in the adjoining discs. Disc injury group A included 17 patients and no disc injury group included 21 patients. Clinical and radiologic parameters were evaluated before surgery, after surgery, and at follow-up. Clinical outcomes included visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, incidence of complications, and incidence of implant failure. Radiologic assessment was accomplished with the Cobb angle (CA), local kyphosis (LK), percentage of anterior vertebral height (AVBH%), intervertebral disc height, and intervertebral disc angle. Fisher's precision probability tests were employed and chi square test were used to compare categorical variables. Paired sample t tests and independent-sample t tests were used to compare continuous data.
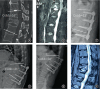
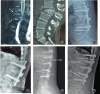
Results: Disc injury mainly involved the cranial disc (15/19, 78.9%). The mean follow-up period for the patients was 30.2 ± 20.1 months. No neurologic deterioration was reported in the patients at the last follow-up. Radiological outcomes at the last follow-up showed significant differences in the CA (18.59° ± 13.74° vs 8.16° ± 9.99°, P = 0.008), LK (12.74° ± 8.00° vs 6.55° ± 4.89°, P = 0.006), and %AVBH (77.16% vs 90.83%, P = 0.01) between the two groups.Implant failure occurred after posterior fixation in five patients with disc injury who did not undergo interbody fusion during the initial surgery. Additionally, in the subgroup analysis, interbody fusion in the implant failure group were significantly different than in the no implant failure group (0% vs 75%, P = 0.009).
Conclusions: AO B2 fracture patients with disc injury have higher risk of complications, especially implant failure after posterior surgery. Interbody fusion should be considered in AO type B2 fracture patients with disc injury.
Keywords: Disc injury; Flexion distraction injury; Posterior surgery; Thoracolumbar fracture.
© 2022 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Herniation of intervertebral disc into thoracolumbar fracture vertebral body leads to malunion of fracture and decrease of intervertebral space height].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023 Jun 25;36(6):532-42. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2023.06.007. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023. PMID: 37366095 Chinese.
-
Correction loss following short-segment posterior fixation for traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures related to endplate and intervertebral disc destruction.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Mar 8;24(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06288-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 36890495 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior fixation including the fractured vertebra for severe unstable thoracolumbar fractures.Spine J. 2015 Feb 1;15(2):256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Spine J. 2015. PMID: 25245505
-
Analysis of intervertebral discs adjacent to thoracolumbar A3 fractures treated by percutaneous instrumentation and kyphoplasty.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Oct;106(6):1221-1226. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.05.006. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32888918 Review.
-
Combined pedicle screw fixation at the fracture vertebrae versus conventional method for thoracolumbar fractures: A meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2018 May;53:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 11. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29535015 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopy-assisted anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with internal fixation vs conventional surgery in the treatment of cervical disc herniation.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2024 Jul 31;19(3):399-406. doi: 10.20452/wiitm.2024.17888. eCollection 2024 Oct 16. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2024. PMID: 40041109 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectiveness of sagittal top compression reduction technique in treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Oct 15;37(10):1246-1252. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202306020. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37848320 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Impact of traumatic intervertebral disc injury on loss of correction following pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 23;26(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08759-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40410692 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous multilevel lumbar pediculolysis associated with spondylolysis: a rare case and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 21;25(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08084-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39574019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abudou M, Chen X, Kong X, Wu T. Surgical versus non‐surgical treatment for thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;6:Cd005079. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

