Simplified PI-RADS (S-PI-RADS) for biparametric MRI to detect and manage prostate cancer: What urologists need to know
- PMID: 35929870
- PMCID: PMC8260088
- DOI: 10.5152/tud.2021.21004
Simplified PI-RADS (S-PI-RADS) for biparametric MRI to detect and manage prostate cancer: What urologists need to know
Abstract
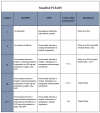
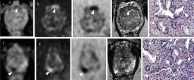
Biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (bpMRI) of the prostate has emerged as an alternative to multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa). However, while the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is widely known for mpMRI, a proper PI-RADS for bpMRI has not yet been adopted. In this review, we report the current status and the future directions of bpMRI, and propose a simplified PI-RADS (S-PI-RADS) that could help radiologists and urologists in the detection and management of PCa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Drost FH, Osses D, Nieboer D, Bangma CH, Steyerberg EW, Roobol MJ, et al. Prostate magnetic resonance imaging, with or without magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy, and systematic biopsy for detecting prostate cancer: a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2020;77:78–94. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.06.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bjurlin MA, Carroll PR, Eggener S, Fulgham PF, Margolis DJ, Pinto PA, et al. Update of the standard operating procedure on the use of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis, staging and management of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2020;203:706–12. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
