Focus on adrenal and related causes of hypertension in childhood and adolescence: Rare or rarely recognized?
- PMID: 35929903
- PMCID: PMC10118774
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000507
Focus on adrenal and related causes of hypertension in childhood and adolescence: Rare or rarely recognized?
Abstract
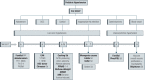
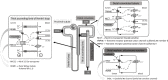
High blood pressure (BP) is not restricted to adults; children and adolescents may also be affected, albeit less frequently. Aside from unfavorable environmental factors, such as obesity and sedentary life leading to early-onset essential hypertension (HT), several secondary causes must be investigated in the occasional hypertensive child/adolescent. Endocrine causes are relevant and multiple, related to the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, gonads, insulin, and others, but generally are associated with adrenal disease. This common scenario has several vital components, such as aldosterone, deoxycorticosterone (DOC), cortisol, or catecholamines, but there are also monogenic disorders involving the kidney tubule that cause inappropriate salt retention and HT that simulate adrenal disease. Finally, a blood vessel disease was recently described that may also participate in this vast spectrum of pediatric hypertensive disease. This review will shed some light on the diagnosis and management of conditions, focusing on the most prevalent adrenal (or adrenal-like) disturbances causing HT.
Keywords: Hypertension; adrenal; childhood.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Congenital adrenal hyperplasia].Med Pregl. 1999 Nov-Dec;52(11-12):447-54. Med Pregl. 1999. PMID: 10748766 Review. Croatian.
-
Investigating mineralocorticoid hypertension.J Hypertens Suppl. 2003 May;21(2):S25-30. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200305002-00005. J Hypertens Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12929904 Review.
-
11-Deoxycorticosterone Producing Adrenal Hyperplasia as a Very Unusual Cause of Endocrine Hypertension: Case Report and Systematic Review of the Literature.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 31;13:846865. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.846865. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35432204 Free PMC article.
-
Inappropriate elevation of the aldosterone/plasma renin activity ratio in hypertensive patients with increases of 11-deoxycorticosterone and 18-hydroxy-11-deoxycorticosterone: a subtype of essential hypertension?Cardiology. 1991;78(2):99-110. doi: 10.1159/000174773. Cardiology. 1991. PMID: 2070375
-
Partial deficiency of adrenal 11-hydroxylase. A possible cause of primary hypertension.Hypertension. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):204-10. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.2.204. Hypertension. 1985. PMID: 2984117
Cited by
-
Is Family History for the Management of Cardiovascular Health in Youth Still Relevant in Clinical Practice?Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Nov;26(11):629-637. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01232-4. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 39190218 Review.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67–e492. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JT, Falkner BE. New Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Hypertension. 2017;70(4):683–686. - PubMed
-
- Guzman-Limon M, Samuels J. Pediatric Hypertension: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019;66(1):45–57. - PubMed
-
- New MI, Geller DS, Fallo F, Wilson RC. Monogenic low renin hypertension. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16(3):92–97. - PubMed
-
- Ceccato F, Mantero F. Monogenic Forms of Hypertension. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2019;48(4):795–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
