Lipid accumulation induced by APOE4 impairs microglial surveillance of neuronal-network activity
- PMID: 35931030
- PMCID: PMC9623845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.07.005
Lipid accumulation induced by APOE4 impairs microglial surveillance of neuronal-network activity
Abstract
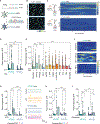
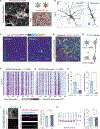
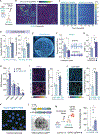
Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) is the greatest known genetic risk factor for developing sporadic Alzheimer's disease. How the interaction of APOE4 microglia with neurons differs from microglia expressing the disease-neutral APOE3 allele remains unknown. Here, we employ CRISPR-edited induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to dissect the impact of APOE4 in neuron-microglia communication. Our results reveal that APOE4 induces a lipid-accumulated state that renders microglia weakly responsive to neuronal activity. By examining the transcriptional signatures of APOE3 versus APOE4 microglia in response to neuronal conditioned media, we established that neuronal cues differentially induce a lipogenic program in APOE4 microglia that exacerbates pro-inflammatory signals. Through decreased uptake of extracellular fatty acids and lipoproteins, we identified that APOE4 microglia disrupts the coordinated activity of neuronal ensembles. These findings suggest that abnormal neuronal network-level disturbances observed in Alzheimer's disease patients harboring APOE4 may in part be triggered by impairment in lipid homeostasis in non-neuronal cells.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer’s risk variant; GIRKs; calcium dynamics; forebrain spheroids; lipid droplet; microglia; network-activity; stem cells.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Neighborhood matters: Altered lipid metabolism in APOE4 microglia causes problems for neurons.Cell Stem Cell. 2022 Aug 4;29(8):1159-1160. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.07.001. Cell Stem Cell. 2022. PMID: 35931027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boscia F, Esposito CL, Casamassa A, de Franciscis V, Annunziato L, and Cerchia L (2013). The isolectin IB4 binds RET receptor tyrosine kinase in microglia. J. Neurochem. 126, 428–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

