Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cancer-related fatigue: associations and effects on depression, anxiety, functional capacity and health-related quality of Life in breast cancer survivors during adjuvant endocrine therapy
- PMID: 35933326
- PMCID: PMC9357315
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09962-x
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cancer-related fatigue: associations and effects on depression, anxiety, functional capacity and health-related quality of Life in breast cancer survivors during adjuvant endocrine therapy
Abstract
Background: The adjuvant treatment with Aromatase Inhibitor (AI) is considered standard of care for postmenopausal breast cancer (BC) women with hormone receptor-positive (HR +), however, it often causes adverse effects such as cancer-related fatigue (CRF). The high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in postmenopausal women who start adjuvant AI supports the hypothesis that hypovitaminosis D would be one of the biological explanations for toxicity of AI. This study aimed to identify the relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] and CRF, and to analyze their associations and effects on depression, anxiety, functional disability, muscle/joint aches and HRQL.
Methods: This prospective study included 89 postmenopausal women diagnosed with HR + early BC in adjuvant endocrine therapy with AI. Anthropometric and body composition assessments were performed, as well as dietary assessments by application of 24-h dietary recall, at three time points, totaling 24 months of follow-up. The women completed the Cervantes Scale (CS), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ). The CRF was determined from the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-fatigue (FACIT-F). The serum 25(OH)D was determined by electrochemiluminescence, with cut-off point above 75 nmol/L adopted as sufficiency. Generalized Linear Model (GLzM) and Generalized Mixed Model (GMM) analysis were used.
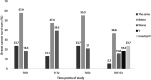
Results: At baseline, 36% (n = 32) of the women presented CRF and 39.3% (n = 35) had 25(OH)D below 75 nmol/L. None of the women reached the Estimated Average Requirements (EAR) of vitamin D. The causality between 25(OH)D and CRF was not significant. Longitudinally, lower levels of 25(OH)D had a negative effect on anxiety (p = 0.020), Menopause and Health (p = 0.033) and Vasomotor scores (p = 0.007). Also, the CRF had a negative effect on anxiety (p = 0.028); depression (p = 0.027); functional disability (p = 0.022); HRQL (p = 0.007); Menopause and Health (p = 0.042), Psychological (p = 0.008) and Couple Relations (p = 0.008) domains; and on Health (p = 0.019) and Aging (p = 0.036) subdomains. Vasomotor subdomain (β = -2.279, p = 0.045) and muscle/joint aches (β = -0.779, p = 0.013) were significant with CRF only at baseline.
Conclusions: This study found negative effect of body adiposity on CRF. Still, the clinical relevance of 25(OH)D and CRF is highlighted, especially that of CRF, considering the consistent impact on several adverse effects reported by BC survivors during adjuvant endocrine therapy.
Keywords: Aromatase Inhibitors; Breast neoplasms; Cancer survivors; Fatigue; Health-related quality of life; Vitamin D deficiency.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-Related quality of life by 31-item Cervantes scale in breast cancer survivors undergoing adjuvant endocrine therapy.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Feb 6;79:100324. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100324. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 38325021 Free PMC article.
-
Menopausal symptoms in breast cancer survivors on adjuvant endocrine therapy compared with those of menopausal women.Maturitas. 2025 Jan;191:108143. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2024.108143. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Maturitas. 2025. PMID: 39500126
-
Prevalence and Predictors of Low Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D among Female African-American Breast Cancer Survivors.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018 Apr;118(4):568-577. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2017.10.009. Epub 2018 Jan 2. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018. PMID: 29305131 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-related Fatigue in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Review.Clin Breast Cancer. 2021 Feb;21(1):10-25. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32819836 Review.
-
The Effect of Exercise on the Alleviation of Side Effects Induced by Aromatase Inhibitors in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Patients.Curr Oncol Rep. 2020 Aug 15;22(11):110. doi: 10.1007/s11912-020-00971-2. Curr Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32803384 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights and implications of sexual dimorphism in osteoporosis.Bone Res. 2024 Feb 18;12(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00306-4. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 38368422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and Health-Related Quality-of-Life Measures in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Longitudinal Study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022 Dec 5;31(12):2126-2135. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-0343. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022. PMID: 36126952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today. Accessed 17 Sep 2021.
-
- Smith I, Dowsett M. Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

