Nanobodies; new molecular instruments with special specifications for targeting, diagnosis and treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35933373
- PMCID: PMC9357333
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02665-0
Nanobodies; new molecular instruments with special specifications for targeting, diagnosis and treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
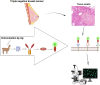
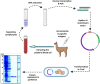
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women and the second leading cause of cancer death in female. Triple-negative breast cancer has a more aggressive proliferation and a poorer clinical diagnosis than other breast cancers. The most common treatments for TNBC are chemotherapy, surgical removal, and radiation therapy, which impose many side effects and costs on patients. Nanobodies have superior advantages, which makes them attractive for use in therapeutic agents and diagnostic kits. There are numerous techniques suggested by investigators for early detection of breast cancer. Nevertheless, there are fewer molecular diagnostic methods in the case of TNBC due to the lack of expression of famous breast cancer antigens in TNBC. Although conventional antibodies have a high ability to detect tumor cell markers, their large size, instability, and costly production cause a lot of problems. Since the HER-2 do not express in TNBC diagnosis, the production of nanobodies for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer cells should be performed against other antigens expressed in TNBC. In this review, nanobodies which developed against triple negative breast cancer, were classified based on type of antigen.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Nanobody; TNBC; Treatment; VHH.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of anti-membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase nanobodies as immunoPET probes for triple negative breast cancer imaging.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 24;9:1058455. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1058455. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36507540 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobodies: a tool to open new horizons in diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Oct 30;21(1):580. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02285-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34717636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2017 Dec 18;35(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-1071-6. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29255938 Review.
-
Knockdown of Kinase Family 15 Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation In vitro and its Clinical Relevance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2019;19(2):147-155. doi: 10.2174/1566524019666190308122108. Curr Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30854965
-
Targeting EGFR of triple-negative breast cancer enhances the therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel- and cetuximab-conjugated nanodiamond nanocomposite.Acta Biomater. 2019 Mar 1;86:395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.01.025. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30660004
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of a broadly neutralizing and protective nanobody against the HA1 domain of H5 avian influenza virus hemagglutinin.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0209024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02090-24. Epub 2025 Apr 7. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40192291 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobodies for the Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13687. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213687. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430166 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 expression in breast cancer and its distinct upregulation in triple-negative breast cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(7):867-894. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.867. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39071464 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobody engineering: computational modelling and design for biomedical and therapeutic applications.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Feb;15(2):236-253. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13850. Epub 2024 Jun 19. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 38898362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of anti-membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase nanobodies as immunoPET probes for triple negative breast cancer imaging.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 24;9:1058455. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1058455. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36507540 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

