The association between Toxoplasma infection and mortality: the NHANES epidemiologic follow-up study
- PMID: 35933421
- PMCID: PMC9357320
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-022-05398-1
The association between Toxoplasma infection and mortality: the NHANES epidemiologic follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma gondii has been reported to be associated with higher mortality in patients with schizophrenia. This study aimed to explore the relationship between T. gondii infection and 25-year mortality based on data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) database.
Methods: Cases with serum T. gondii antibody test results were included in this study and the corresponding mortality dataset was obtained from the US National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to match age and sex between groups. The Cox proportional hazards model was used to evaluate the effect of T. gondii infection on mortality.
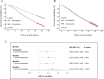
Results: A total of 14,181 cases were included in the analysis, of which 3831 (27.0%) were seropositive for T. gondii antibody. The median follow-up time of the whole cohort was 22.5 (interquartile range 16.3, 24.5) years. A total of 5082 deaths were observed in this cohort, a mortality rate of 35.8%. All-cause mortality was significantly higher in the seropositive group than in the seronegative group (50.0% vs 30.6%, P < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a significant difference in the survival time between two groups before and after PSM. Multivariate analysis showed that T. gondii infection was independently associated with higher all-cause mortality after adjusting for potential confounders.
Conclusions: Toxoplasma gondii infection is associated with higher mortality in general population.
Keywords: Mortality; NHANES; Toxoplasma gondii; Toxoplasmosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma Gondii infection and cardiovascular mortality: sex-specific differences in a United States population-based cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):1029. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09934-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39333926 Free PMC article.
-
Drinking water source and human Toxoplasma gondii infection in the United States: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data.BMC Public Health. 2014 Jul 10;14:711. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-711. BMC Public Health. 2014. PMID: 25012250 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Toxoplasma gondii IgG and Liver Injury in US Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 19;19(12):7515. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127515. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742764 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2019 Apr;129:30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.01.040. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30708042
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection and spontaneous abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2021 Sep;158:105070. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105070. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34186117
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Patients Diagnosed with Schizophrenia: A Case-Control Cross Sectional Study.Biomedicines. 2024 May 1;12(5):998. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12050998. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790960 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of Toxoplasma gondii in periodontal diseases and underlying mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 3;15:1464108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464108. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39430742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Development of Adenovirus-Vectored Vaccines for Parasitic Infections.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;16(3):334. doi: 10.3390/ph16030334. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Nrf2 signaling in parasitic diseases and its therapeutic potential.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 14;10(12):e32459. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32459. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38988513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age and ocular toxoplasmosis: a narrative review.FEMS Microbes. 2025 Feb 26;6:xtaf002. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtaf002. eCollection 2025. FEMS Microbes. 2025. PMID: 40098631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

