Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome induced by propylthiouracil: case report and literature review
- PMID: 35933436
- PMCID: PMC9357314
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-022-00707-w
Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome induced by propylthiouracil: case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) is a rare, potentially life-threatening systemic drug reaction. Antithyroid drugs (ATDs) causing DIHS have seldom been reported before.
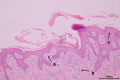
Case presentation: We present a case of propylthiouracil (PTU)-induced DIHS, which included fever, skin rash, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, serious liver and kidney dysfunction, peripheral blood eosinophilia, and atypical lymphocytosis. Following supportive therapy, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and systemic corticosteroid, the patient experienced a resolution of fever and rash combined with progressive normalization of hematological index and organ function. These clinical features, and the skin lesion biopsy confirmed DIHS diagnosis.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the second reported case of PTU-induced DIHS worldwide and the first human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing of PTU-induced DIHS. Clinicians should cautiously distinguish hyperthyroidism etiology and identify the indication of ATDs. Timely recognition and formal DIHS treatment are required in patients with ATDs.
Keywords: Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome; Human leukocyte antigen; Propylthiouracil.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DRESS/DiHS syndrome induced by Propylthiouracil: a case report.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01273-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 36691013 Free PMC article.
-
Literature review of the clinical features of sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS/DIHS).Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 2;15:1488483. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1488483. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39687296 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome due to phenytoin: Case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 27;103(39):e39715. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039715. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39331866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case report: Sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 24;10:1140339. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1140339. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37293296 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome to BRAF inhibitors with and without previous immune checkpoint inhibition: a review.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Mar;30(3):2839-2851. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06543-9. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34546454 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Manifestations of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome: A Systematic Review of 71 Cases.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 10;12(14):4576. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144576. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37510691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Socioeconomic and environmental determinants of asthma prevalence: a cross-sectional study at the U.S. County level using geographically weighted random forests.Int J Health Geogr. 2023 Aug 10;22(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12942-023-00343-6. Int J Health Geogr. 2023. PMID: 37563691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Liss Y, Chu CY, Creamer D, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071–1080. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12501. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

