Proteomics analysis of chronic skin injuries caused by mustard gas
- PMID: 35933451
- PMCID: PMC9357330
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-022-01328-3
Proteomics analysis of chronic skin injuries caused by mustard gas
Abstract
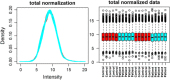
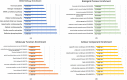
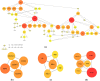
Sulfur mustard (SM) is an alkylating and forming chemical that was widely used by Iraqi forces during the Iran-Iraq wars. One of the target organs of SM is the skin. Understanding the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of SM may help better identify complications and find appropriate treatments. The current study collected ten SM-exposed patients with long-term skin complications and ten healthy individuals. Proteomics experiments were performed using the high-efficiency TMT10X method to evaluate the skin protein profile, and statistical bioinformatics methods were used to identify the differentially expressed proteins. One hundred twenty-nine proteins had different expressions between the two groups. Of these 129 proteins, 94 proteins had increased expression in veterans' skins, while the remaining 35 had decreased expression. The hub genes included RPS15, ACTN1, FLNA, HP, SDHC, and RPL29, and three modules were extracted from the PPI network analysis. Skin SM exposure can lead to oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and cell proliferation.
Keywords: Chemical agents; Chemical injuries; Mustard gas; Proteomics analysis; Systems biology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health assessment of sulfur mustard-chemical veterans with various respiratory diseases: The result of a comparative analysis of biological health scores (BHS) through 50 biomarkers.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;145:113767. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113767. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39642570
-
Tear proteomics analysis of patient suffered from delayed mustard gas keratopathy.Proteome Sci. 2022 Aug 10;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12953-022-00195-1. Proteome Sci. 2022. PMID: 35948930 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur mustard and biological ageing: A multisystem biological health score approach as an extension of the allostatic load in Sardasht chemical veterans.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108375. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108375. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34810125
-
Cutaneous and ocular late complications of sulfur mustard in Iranian veterans.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2007;26(2):73-81. doi: 10.1080/15569520701212399. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17612976 Review.
-
Historical perspective on effects and treatment of sulfur mustard injuries.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Dec 5;206(3):512-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23816402 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of mustard lung as a complicated disease using systems biology approach.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Nov 23;22(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02240-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36419000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith KJ, et al. Sulfur mustard: its continuing threat as a chemical warfare agent, the cutaneous lesions induced, progress in understanding its mechanism of action, its long-term health effects, and new developments for protection and therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(5):765–776. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(95)91457-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pechura CM, Rall DP. Dermatological effects of mustard agents and lewisite, in veterans at risk: the health effects of mustard gas and lewisite. National Academies Press (US); 1993. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

