Caveolin-1 identified as a key mediator of acute lung injury using bioinformatics and functional research
- PMID: 35933468
- PMCID: PMC9357074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05134-8
Caveolin-1 identified as a key mediator of acute lung injury using bioinformatics and functional research
Abstract
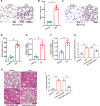
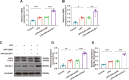
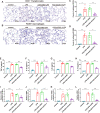
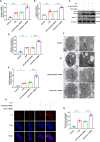
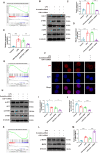
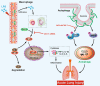
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a potentially life-threatening, devastating disease with an extremely high rate of mortality. The underlying mechanism of ALI is currently unclear. In this study, we aimed to confirm the hub genes associated with ALI and explore their functions and molecular mechanisms using bioinformatics methods. Five microarray datasets available in GEO were used to perform Robust Rank Aggregation (RRA) to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and the key genes were identified via the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. Lipopolysaccharide intraperitoneal injection was administered to establish an ALI model. Overall, 40 robust DEGs, which are mainly involved in the inflammatory response, protein catabolic process, and NF-κB signaling pathway were identified. Among these DEGs, we identified two genes associated with ALI, of which the CAV-1/NF-κB axis was significantly upregulated in ALI, and was identified as one of the most effective targets for ALI prevention. Subsequently, the expression of CAV-1 was knocked down using AAV-shCAV-1 or CAV-1-siRNA to study its effect on the pathogenesis of ALI in vivo and in vitro. The results of this study indicated that CAV-1/NF-κB axis levels were elevated in vivo and in vitro, accompanied by an increase in lung inflammation and autophagy. The knockdown of CAV-1 may improve ALI. Mechanistically, inflammation was reduced mainly by decreasing the expression levels of CD3 and F4/80, and activating autophagy by inhibiting AKT/mTOR and promoting the AMPK signaling pathway. Taken together, this study provides crucial evidence that CAV-1 knockdown inhibits the occurrence of ALI, suggesting that the CAV-1/NF-κB axis may be a promising therapeutic target for ALI treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in rats by inhibition of caveolin-1 downstream signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109314. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109314. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31545263
-
[Multiple components of Mahuang Shengma Decoction on prevention and treatment of acute lung injury based on RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Nov;46(21):5693-5700. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210802.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34951223 Chinese.
-
Baicalin exerts protective effects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the crosstalk between the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis and NF-κB pathway in CX3CL1-knockout mice.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Mar;37(3):703-15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2456. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26782291 Free PMC article.
-
The critical roles of caveolin-1 in lung diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1417834. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1417834. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39380904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR and autophagy in acute lung injury pathogenesis and therapeutic potential.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Apr 30;17(4):2679-2692. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1817. Epub 2025 Apr 21. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40400934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Administration of turmeric kombucha ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by attenuating inflammation and modulating gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1452190. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1452190. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282561 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar-capillary endocytosis and trafficking in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1360370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360370. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38533500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-packaged GBP2 from macrophages aggravates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting ferroptosis in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells.Redox Biol. 2025 May;82:103614. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103614. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40156957 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular markers of type II alveolar epithelial cells in acute lung injury by bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 18;13(1):17797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45129-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37853056 Free PMC article.
-
B2M is a Biomarker Associated With Immune Infiltration In High Altitude Pulmonary Edema.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(1):168-185. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230510095840. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37165489 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

