Correlation of tumour subtype with long-term outcome in small breast carcinomas: a Swedish population-based retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 35933487
- PMCID: PMC9464733
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-022-06691-4
Correlation of tumour subtype with long-term outcome in small breast carcinomas: a Swedish population-based retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate if molecular subtype is associated with outcome in stage 1 breast cancer (BC).
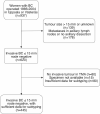
Methods: Tissue samples from 445 women with node-negative BC ≤ 15 mm, treated in 1986-2004, were classified into surrogate molecular subtypes [Luminal A-like, Luminal B-like (HER2-), HER2-positive, and triple negative breast cancer (TNBC)]. Information on treatment, recurrences, and survival were gathered from medical records.
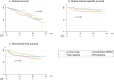
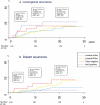
Results: Tumour subtype was not associated with overall survival (OS). Luminal B-like (HER2-) and TNBC were associated with higher incidence of distant metastasis at 20 years (Hazard ratio (HR) 2.26; 95% CI 1.08-4.75 and HR 3.24; 95% CI 1.17-9.00, respectively). Luminal B-like (HER2-) and TNBC patients also had worse breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS), although not statistically significant (HR 1.53; 95% CI 0.70-3.33 and HR 1.89; 95% CI 0.60-5.93, respectively). HER2-positive BC was not associated with poor outcome despite no patient receiving HER2-targeted therapy, with most of these tumours being ER+.
Conclusions: Stage 1 TNBC or Luminal B-like (HER2-) tumours behave more aggressively. Women with HER2+/ER+ tumours do not have an increased risk of distant metastasis or death, absent targeted treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Long-term outcome; Molecular subtypes; TMA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(19):10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im Y-H, Roman L, Tseng L-M, Liu M-C, Lluch A, Staroslawska E, de la Haba-Rodriguez J, Im S-A, et al. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): a randomised multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70336-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MCU, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, Dumontet C, Reed J, Krajewska M, Treilleux I, Rupin M, et al. Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1168–1176. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous