Association between serum vitamin D levels and age in patients with epilepsy: a retrospective study from an epilepsy center in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 35933609
- PMCID: PMC9357294
- DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.2022.262
Association between serum vitamin D levels and age in patients with epilepsy: a retrospective study from an epilepsy center in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to various medical conditions such as bone loss, decreased mineralization, endocrine disorders, and central nervous system disorders, including epilepsy. Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent among patients with epilepsy (PWE). However, the specific association between vitamin D levels and age in PWE is unclear.
Objectives: Identify the relation between vitamin D level and age in PWE and evaluate factors that may play a role in seizure control.
Design: Retrospective analytical medical record review SETTING: Outpatient epilepsy research clinic in Saudi Arabia PATIENTS AND METHODS: Between November 2016 and April 2020, we selected eligible PWE aged older than 14 years whose vita-min D levels were recorded at least once after reviewing 1550 patient electronic files. We analyzed data on serum vitamin D level by age and other factors, vitamin D supplement use, seizure classification, and conducted a multivariate logistic regression to assess associations with seizure control.
Main outcome measures: Relationships between vitamin D levels and age and factors that might affect seizure control.
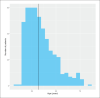
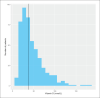
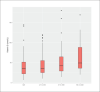
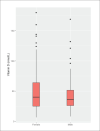
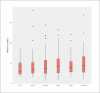
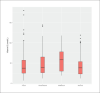
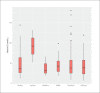
Sample size: 524 patients RESULTS: The prevalence of low serum vitamin D levels was high (86.8%). The median vitamin D level in all patients was low (38 nmol/L), and was lower in young PWE than in adult PWE (P<.01). Only 146 patients received vitamin D supplements. High vitamin D levels were associated with a 40% seizure reduction.
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency is underestimated in PWE in Saudi Arabia, and is more prevalent among young adults and patients on polytherapy than in other PWE. Patients with high vitamin D levels had good seizure control compared with those with low levels. The effect of vitamin D supplements on seizure control should be further investigated in randomized control trials.
Limitations: Retrospective study and no categorization by presence of supplementation.
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on: Association between serum vitamin D levels and age in patients with epilepsy: A retrospective study from an epilepsy center in Saudi Arabia.Ann Saudi Med. 2023 Jan-Feb;43(1):62. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2023.62. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Ann Saudi Med. 2023. PMID: 36739501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Patients' knowledge about epilepsy in a tertiary medical center: A cross-sectional study from Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 Mar;116:107395. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107395. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 33640295
-
Calcium metabolism serum markers in adult patients with epilepsy and the effect of vitamin D supplementation on seizure control.Seizure. 2018 May;58:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Seizure. 2018. PMID: 29674238
-
Knowledge and attitudes about vitamin D, and behaviors related to vitamin D in adults with and without coronary heart disease in Saudi Arabia.BMC Public Health. 2017 Mar 16;17(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4183-1. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28302087 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D status correction in Saudi Arabia: an experts' consensus under the auspices of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO).Arch Osteoporos. 2017 Dec;12(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s11657-016-0295-y. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Arch Osteoporos. 2017. PMID: 28004295 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D prophylaxis in persons with epilepsy?Epilepsia. 2024 Sep;65(9):2567-2579. doi: 10.1111/epi.18046. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Epilepsia. 2024. PMID: 39494692 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Strategies to Ameliorate Neuronal Damage in Epilepsy by Regulating Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Neuroinflammation.Brain Sci. 2023 May 11;13(5):784. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050784. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demographics, Clinical Characteristics, and Management Strategies of Epilepsy in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Jun 29;16(6):e63436. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63436. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39077233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective and inflammatory biomarkers in pediatric drug-resistant epilepsy: Interplay between GDNF, IL-1β and vitamin D 25-OH.Narra J. 2024 Dec;4(3):e1581. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i3.1581. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39816124 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Vitamin D on Neurological and Mental Disorders.Diseases. 2024 Jun 20;12(6):131. doi: 10.3390/diseases12060131. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 38920563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D content and prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in patients with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 30;11:1439279. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1439279. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39279896 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

