X chromosomes show relaxed selection and complete somatic dosage compensation across Timema stick insect species
- PMID: 35933721
- PMCID: PMC10087215
- DOI: 10.1111/jeb.14075
X chromosomes show relaxed selection and complete somatic dosage compensation across Timema stick insect species
Abstract
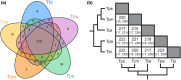
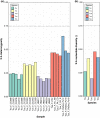
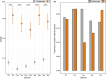
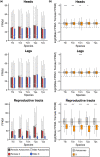
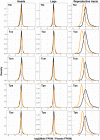
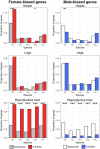
Sex chromosomes have evolved repeatedly across the tree of life. As they are present in different copy numbers in males and females, they are expected to experience different selection pressures than the autosomes, with consequences including a faster rate of evolution, increased accumulation of sexually antagonistic alleles and the evolution of dosage compensation. Whether these consequences are general or linked to idiosyncrasies of specific taxa is not clear as relatively few taxa have been studied thus far. Here, we use whole-genome sequencing to identify and characterize the evolution of the X chromosome in five species of Timema stick insects with XX:X0 sex determination. The X chromosome had a similar size (approximately 12% of the genome) and gene content across all five species, suggesting that the X chromosome originated prior to the diversification of the genus. Genes on the X showed evidence of relaxed selection (elevated dN/dS) and a slower evolutionary rate (dN + dS) than genes on the autosomes, likely due to sex-biased mutation rates. Genes on the X also showed almost complete dosage compensation in somatic tissues (heads and legs), but dosage compensation was absent in the reproductive tracts. Contrary to prediction, sex-biased genes showed little enrichment on the X, suggesting that the advantage X-linkage provides to the accumulation of sexually antagonistic alleles is weak. Overall, we found the consequences of X-linkage on gene sequences and expression to be similar across Timema species, showing the characteristics of the X chromosome are surprisingly consistent over 30 million years of evolution.
Keywords: insects; population genetics; sex chromosomes; sexual selection & conflicts.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Evolutionary Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society for Evolutionary Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of X chromosome hyper-expression and inactivation in male tissues during stick insect development.PLoS Genet. 2025 Mar 10;21(3):e1011615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011615. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40063618 Free PMC article.
-
Disentangling the Causes for Faster-X Evolution in Aphids.Genome Biol Evol. 2018 Feb 1;10(2):507-520. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy015. Genome Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29360959 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation and sex-specific epigenetic landscape of the X chromosome in the pea aphid.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017 Jun 15;10:30. doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0137-1. eCollection 2017. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017. PMID: 28638443 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation of the sex chromosomes and autosomes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27112542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parallel Universes for Models of X Chromosome Dosage Compensation in Drosophila: A Review.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2016;148(1):52-67. doi: 10.1159/000445924. Epub 2016 May 12. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 27166165 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Chromosome Dosage Compensation in Insects.Insects. 2025 Feb 4;16(2):160. doi: 10.3390/insects16020160. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40003790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome-scale genome of the polyphagous pest Anastrepha ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae) provides insights on sex chromosome evolution in Anastrepha.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Oct 4;14(12):jkae239. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae239. Online ahead of print. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 39365162 Free PMC article.
-
Genome of the Lord Howe Island Stick Insect Reveals a Highly Conserved Phasmid X Chromosome.Genome Biol Evol. 2023 Jun 1;15(6):evad104. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evad104. Genome Biol Evol. 2023. PMID: 37279506 Free PMC article.
-
Two novel genomes of fireflies with different degrees of sexual dimorphism reveal insights into sex-biased gene expression and dosage compensation.Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 27;7(1):906. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06550-6. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39068254 Free PMC article.
-
The grasshopper genome reveals long-term gene content conservation of the X Chromosome and temporal variation in X Chromosome evolution.Genome Res. 2024 Aug 20;34(7):997-1007. doi: 10.1101/gr.278794.123. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39103228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbuthnott, D. , Crespi, B. J. , & Schwander, T. (2015). Female stick insects mate multiply to find compatible mates. The American Naturalist, 186, 519–530. - PubMed
-
- Axelsson, E. , Smith, N. G. C. , Sundström, H. , Berlin, S. , & Ellegren, H. (2004). Male‐biased mutation rate and divergence in autosomal, Z‐linked and W‐linked introns of chicken and Turkey. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 21, 1538–1547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

