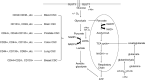
Concise review: Cancer cell reprogramming and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 35933935
- PMCID: PMC9364012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101503
Concise review: Cancer cell reprogramming and therapeutic implications
Abstract
The cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis postulates that cancer originates from the malignant transformation of stem cells and is considered to apply to a variety of cancers. Additionally, cancer cells alter metabolic processes to sustain their characteristic uncontrolled growth and proliferation. Further, microRNAs (miRNAs) are found to be involved in acquisition of stem cell-like properties, regulation and reprogramming of cancer cells during cancer progression through its post-transcriptional-regulatory activity. In this concise review, we aim to integrate the current knowledge and recent advances to elucidate the mechanisms involved in the regulation of cell reprogramming and highlights the potential therapeutic implications for the future.
Keywords: CSC; Cancer cell reprogramming; Metabolic reprogramming; miRNA.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer cell reprogramming to identify the genes competent for generating liver cancer stem cells.Inflamm Regen. 2017 May 18;37:15. doi: 10.1186/s41232-017-0041-x. eCollection 2017. Inflamm Regen. 2017. PMID: 29259714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise Review: LIN28/let-7 Signaling, a Critical Double-Negative Feedback Loop During Pluripotency, Reprogramming, and Tumorigenicity.Cell Reprogram. 2017 Oct;19(5):289-293. doi: 10.1089/cell.2017.0015. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Cell Reprogram. 2017. PMID: 28846452 Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Lung Cancer Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 5;13(7):1716. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071716. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Role of microRNAs in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 31;12(9):2462. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092462. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32878019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear reprogramming of luminal-like breast cancer cells generates Sox2-overexpressing cancer stem-like cellular states harboring transcriptional activation of the mTOR pathway.Cell Cycle. 2013 Sep 15;12(18):3109-24. doi: 10.4161/cc.26173. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23974095 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cinobufacini enhances the therapeutic response of 5-Fluorouracil against gastric cancer by targeting cancer stem cells via AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling axis.Transl Oncol. 2024 Sep;47:102054. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102054. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38970916 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression.Transl Oncol. 2023 Feb;28:101610. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101610. Epub 2022 Dec 24. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36635022 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interplay between Bile Acids and Intestinal Microbiota: Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential for Infections.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 20;13(8):702. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080702. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Single-Cell Multi-Omics to Decode Tumor Microenvironment Diversity and Therapeutic Resistance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 10;18(1):75. doi: 10.3390/ph18010075. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources