Ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by CRISPR-based screen-printed carbon electrode
- PMID: 35934402
- PMCID: PMC9249825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340120
Ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by CRISPR-based screen-printed carbon electrode
Abstract
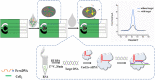
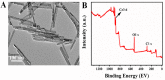
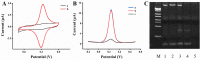
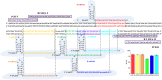
Early and accurate diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 was crucial for COVID-19 control and urgently required ultra-sensitive and rapid detection methods. CRISPR-based detection systems have great potential for rapid SARS-CoV-2 detection, but detecting ultra-low viral loads remains technically challenging. Here, we report an ultrasensitive CRISPR/Cas12a-based electrochemical detection system with an electrochemical biosensor, dubbed CRISPR-SPCE, in which the CRISPR ssDNA reporter was immobilized onto a screen-printed carbon electrode. Electrochemical signals are detected due to CRISPR cleavage, giving enhanced detection sensitivity. CRISPR-SPCE enables ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 detection, reaching as few as 0.27 copies μL-1. Moreover, CRISPR-SPCE is also highly specific and inexpensive, providing a fast and simple SARS-CoV-2 assay.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas12a; CeO(2) nanorods; Detection; SARS-CoV-2; Screen-printed carbon electrode.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

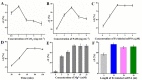
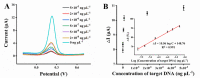
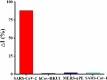
Similar articles
-
Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Highly Specific Diagnosis of COVID-19 by CRISPR-Based Detection.ACS Sens. 2021 Mar 26;6(3):881-888. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01984. Epub 2021 Mar 1. ACS Sens. 2021. PMID: 33645226
-
Imunocapture Magnetic Beads Enhanced and Ultrasensitive CRISPR-Cas13a-Assisted Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 May 31;13(6):597. doi: 10.3390/bios13060597. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366962 Free PMC article.
-
Cas12a-assisted RTF-EXPAR for accurate, rapid and simple detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Nov 15;216:114683. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114683. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 36088673 Free PMC article.
-
Towards application of CRISPR-Cas12a in the design of modern viral DNA detection tools (Review).J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jan 21;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01246-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35062978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Short Review Comparing Carbon-Based Electrochemical Platforms With Other Materials For Biosensing SARS-Cov-2.ChemistrySelect. 2022 Oct 7;7(37):e202202465. doi: 10.1002/slct.202202465. Epub 2022 Oct 4. ChemistrySelect. 2022. PMID: 36711230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Porous GNPs assisted LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a amperometric biosensor as a potential point of care testing system for SARS-CoV-2.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 Apr 7;192(5):280. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07094-0. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40195165
-
Point-of-care CRISPR/Cas biosensing technology: A promising tool for preventing the possible COVID-19 resurgence caused by contaminated cold-chain food and packaging.Food Front. 2022 Oct 12:10.1002/fft2.176. doi: 10.1002/fft2.176. Online ahead of print. Food Front. 2022. PMID: 36712576 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid determination of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid proteins based on 2D/2D MXene/P-BiOCl/Ru(bpy)32+ heterojunction composites to enhance electrochemiluminescence performance.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Nov 22;1234:340522. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340522. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 36328721 Free PMC article.
-
Polyaniline-based electrochemical immunosensor for the determination of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Mar 1;862:160700. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160700. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36493838 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Detection of Alpha-Amylase in Saliva Using Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes: A Promising Biomarker for Clinical Oral Diagnostics.Med Devices (Auckl). 2025 Jan 7;18:15-27. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S493383. eCollection 2025. Med Devices (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 39801672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y.X., Zhang Y., Chen J.B., Wang M.J., Zhang T., Luo W.X., Li Y.L., Wu Y.P., Zeng B., Zhang K.X., Deng R.J., Li W.M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and its mutated variants via CRISPR-cas13-based transcription amplification. Anal. Chem. 2021;93(7):3393–3402. - PubMed
-
- Yang K.F., Chaput J.C. REVEALR: a multicomponent XNAzyme-based nucleic acid detection system for SARS-CoV-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021;143(24):8957–8961. - PubMed
-
- Shan B.J., Broza Y.Y., Li W.J., Wang Y., Wu S.H., Liu Z.Z., Wang J., Gui S.Y., Wang L., Zhang Z.H., Liu W., Zhou S.B., Jin W., Zhang Q.Y., Hu D.D., Lin L., Zhang Q.J., Li W., Wang J.Q., Liu H., Pan Y.Y., Haick H. Multiplexed nanomaterial-based sensor array for detection of COVID-19 in exhaled breath. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):12125–12132. - PubMed
-
- Fozouni P., Son S.M., Derby M.D.D., Knott G.J., Gray C.N., D'Ambrosio M.V., Zhao C.Y., Switz N.A., Kumar G.R., Stephens S.I., Boehm D., Tsou C.-L., Shu J., Bhuiya A., Armstrong M., Harris A.R., Chen P.-Y., Osterloh J.M., Meyer-Franke A., Joehnk B., Walcott K., Sil A., Langelier C., Pollard K.S., Crawford E.D., Puschnik A.S., Phelps M., Kistler A., DeRisi J.L., Doudna J.A., Fletcher D.A., Ott M. Amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas13a and mobile phone microscopy. Cell. 2021;184(2):323–333. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

