Ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by CRISPR-based screen-printed carbon electrode
- PMID: 35934402
- PMCID: PMC9249825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340120
Ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by CRISPR-based screen-printed carbon electrode
Abstract
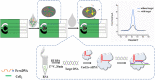
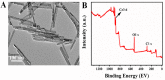
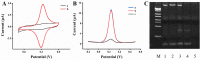
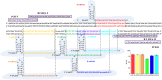
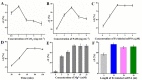
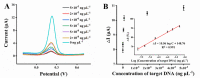
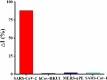
Early and accurate diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 was crucial for COVID-19 control and urgently required ultra-sensitive and rapid detection methods. CRISPR-based detection systems have great potential for rapid SARS-CoV-2 detection, but detecting ultra-low viral loads remains technically challenging. Here, we report an ultrasensitive CRISPR/Cas12a-based electrochemical detection system with an electrochemical biosensor, dubbed CRISPR-SPCE, in which the CRISPR ssDNA reporter was immobilized onto a screen-printed carbon electrode. Electrochemical signals are detected due to CRISPR cleavage, giving enhanced detection sensitivity. CRISPR-SPCE enables ultrasensitive SARS-CoV-2 detection, reaching as few as 0.27 copies μL-1. Moreover, CRISPR-SPCE is also highly specific and inexpensive, providing a fast and simple SARS-CoV-2 assay.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas12a; CeO(2) nanorods; Detection; SARS-CoV-2; Screen-printed carbon electrode.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y.X., Zhang Y., Chen J.B., Wang M.J., Zhang T., Luo W.X., Li Y.L., Wu Y.P., Zeng B., Zhang K.X., Deng R.J., Li W.M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and its mutated variants via CRISPR-cas13-based transcription amplification. Anal. Chem. 2021;93(7):3393–3402. - PubMed
-
- Yang K.F., Chaput J.C. REVEALR: a multicomponent XNAzyme-based nucleic acid detection system for SARS-CoV-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021;143(24):8957–8961. - PubMed
-
- Shan B.J., Broza Y.Y., Li W.J., Wang Y., Wu S.H., Liu Z.Z., Wang J., Gui S.Y., Wang L., Zhang Z.H., Liu W., Zhou S.B., Jin W., Zhang Q.Y., Hu D.D., Lin L., Zhang Q.J., Li W., Wang J.Q., Liu H., Pan Y.Y., Haick H. Multiplexed nanomaterial-based sensor array for detection of COVID-19 in exhaled breath. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):12125–12132. - PubMed
-
- Fozouni P., Son S.M., Derby M.D.D., Knott G.J., Gray C.N., D'Ambrosio M.V., Zhao C.Y., Switz N.A., Kumar G.R., Stephens S.I., Boehm D., Tsou C.-L., Shu J., Bhuiya A., Armstrong M., Harris A.R., Chen P.-Y., Osterloh J.M., Meyer-Franke A., Joehnk B., Walcott K., Sil A., Langelier C., Pollard K.S., Crawford E.D., Puschnik A.S., Phelps M., Kistler A., DeRisi J.L., Doudna J.A., Fletcher D.A., Ott M. Amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas13a and mobile phone microscopy. Cell. 2021;184(2):323–333. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

