Analysis of mechanisms of Shenhuang Granule in treating severe COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 35934629
- PMCID: PMC9328842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.07.005
Analysis of mechanisms of Shenhuang Granule in treating severe COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
Objective: Severe cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are expected to have a worse prognosis than mild cases. Shenhuang Granule (SHG) has been shown to be a safe and effective treatment for severe COVID-19 in a previous randomized clinical trial, but the active chemical constituents and underlying mechanisms of action remain unknown. The goal of this study is to explore the chemical basis and mechanisms of SHG in the treatment of severe COVID-19, using network pharmacology.
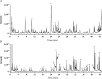
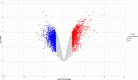
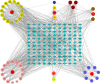
Methods: Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry was employed to screen chemical constituents of SHG. Putative therapeutic targets were predicted by searching traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacology database and analysis platform, SwissTargetPrediction, and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. The target protein-protein interaction network and enrichment analysis were performed to investigate the hub genes and presumptive mechanisms. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations were used to verify the stability and interaction between the key chemical constituents of SHG and COVID-19 protein targets.
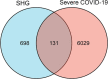
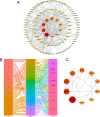
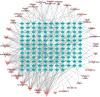
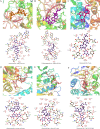
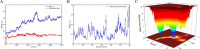
Results: Forty-five chemical constituents of SHG were identified along with 131 corresponding therapeutic targets, including hub genes such as HSP90AA1, MMP9, CXCL8, PTGS2, IFNG, DNMT1, TYMS, MDM2, HDAC3 and ABCB1. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that SHG mainly acted on the neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, calcium signaling pathway and cAMP signaling pathway. Molecular docking showed that the key constituents had a good affinity with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 protein targets. Molecular dynamics simulations indicated that ginsenoside Rg4 formed a stable protein-ligand complex with helicase.
Conclusion: Multiple components of SHG regulated multiple targets to inhibit virus invasion and cytokine storm through several signaling pathways; this provides a scientific basis for clinical applications and further experiments.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mechanism; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation; Network pharmacology; SARS-CoV-2; Shenhuang granule.
Copyright © 2022 Shanghai Changhai Hospital. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Active constituents and mechanisms of Respiratory Detox Shot, a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, for COVID-19 control and prevention: Network-molecular docking-LC-MSE analysis.J Integr Med. 2020 May;18(3):229-241. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2020.03.004. Epub 2020 Apr 8. J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 32307268 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(10):1785-1804. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220523151119. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35616676
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on molecular targets and mechanisms of Huashi Baidu formula in the treatment of COVID-19.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020 Aug;46(8):1345-1353. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2020.1788070. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32643448 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential mechanism of Kaixinsan powder for the same pathogenesis of PTSD and anxiety based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e35869. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035869. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the efficacy and potential pharmacological mechanism of Yupingfeng in treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis and in silico study.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Mar 13;343:119441. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119441. Epub 2025 Feb 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39914688
Cited by
-
Molecular docking and molecular dynamics study Lianhua Qingwen granules (LHQW) treats COVID-19 by inhibiting inflammatory response and regulating cell survival.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1044770. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1044770. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36506032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. (2021-11-11) [2021-11-11]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Attaway A.H., Scheraga R.G., Bhimraj A., Biehl M., Hatipoğlu U. Severe COVID-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management. BMJ. 2021;372 - PubMed
-
- National Health Commission & State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial 8th edition). (2021-4-14) [2021-11-11]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-04/15/content_5599795.htm?_zbs_....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

