Serum gasdermin D levels are associated with the chest computed tomography findings and severity of COVID-19
- PMID: 35934631
- PMCID: PMC9273659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resinv.2022.06.007
Serum gasdermin D levels are associated with the chest computed tomography findings and severity of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The role of programmed cell death, especially pyroptosis and apoptosis, in unfavorable immune responses in COVID-19 remains to be elucidated.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis to investigate the association between the serum gasdermin D (GSDMD) levels, a pyroptotic marker, and caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 fragment (M30), an apoptotic marker, and the clinical status and abnormal chest computed tomography (CT) findings in patients with COVID-19.
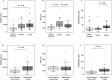
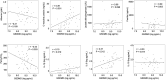
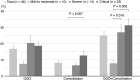
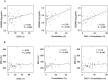
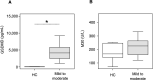
Results: In this study, 46 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were divided into the following three groups according to the disease severity: mild to moderate group (n = 10), severe group (n = 14), and critical group (n = 22). The serum GSDMD levels were higher in the critical group than in the mild to moderate group (P = 0.016). In contrast, serum M30 levels were lower in the critical group than in the severe group (P = 0.048). Patients who required mechanical ventilation or died had higher serum GSDMD levels than those who did not (P = 0.007). Area of consolidation only and of ground glass opacity plus consolidation positively correlated with serum GSDMD levels (r = 0.56, P < 0.001 and r = 0.53, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Higher serum GSDMD levels are associated with critical respiratory status and the consolidation area on chest CT in patients with COVID-19, suggesting that excessive activation of pyroptosis may affect the clinical manifestations in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Apoptosis; COVID-19; Caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 fragment; Gasdermin D; Pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2022 The Japanese Respiratory Society. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gasdermin D is involved in switching from apoptosis to pyroptosis in TLR4-mediated renal tubular epithelial cells injury in diabetic kidney disease.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022 Sep 30;727:109347. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109347. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35809639
-
Gasdermin D serves as a key executioner of pyroptosis in experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model both in vivo and in vitro.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Jun;97(6):645-660. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24385. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 30600840
-
Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death.Nature. 2015 Oct 29;526(7575):660-5. doi: 10.1038/nature15514. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26375003
-
Mechanisms and Therapeutic Regulation of Pyroptosis in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 20;21(4):1456. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041456. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Gasdermin-Mediated Cell Death.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020 Mar 2;12(3):a036400. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036400. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020. PMID: 31451512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of inflammasomes in human diseases and their potential as therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 5;9(1):10. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01687-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38177104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRP3, the inflammasome and COVID-19 infection.QJM. 2023 Jul 28;116(7):502-507. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcad011. QJM. 2023. PMID: 36661317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the effect of serum gasdermin d levels on clinical course and mortality in patients with covid-19.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):893. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11277-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40610919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ivanisenko N.V., Seyrek K., Kolchanov N.A., Ivanisenko V.A., Lavrik I.N. The role of death domain proteins in host response upon SARS-CoV-2 infection: modulation of programmed cell death and translational applications. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:101. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00331-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

