Synthetic Homoisoflavane Derivatives of Cremastranone Suppress Growth of Colorectal Cancer Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Induction of Apoptosis
- PMID: 35934668
- PMCID: PMC9622311
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.090
Synthetic Homoisoflavane Derivatives of Cremastranone Suppress Growth of Colorectal Cancer Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Induction of Apoptosis
Abstract
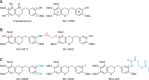
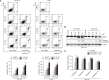
Colorectal cancer is diagnosed as the third most prevalent cancer; thus, effective therapeutic agents are urgently required. In this study, we synthesized six homoisoflavane derivatives of cremastranone and investigated their cytotoxic effects on the human colorectal cancer cell lines HCT116 and LoVo. We further examined the related mechanisms of action using two of the potent compounds, SH-19027 and SHA-035. They substantially reduced the cell viability and proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with SH-19027 and SHA-035 induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and increased expression of p21 both of which are implicated in cell cycle control. In addition, the apoptotic cell population and apoptosis-associated marker expression were accordingly increased. These results suggest that the synthesized cremastranone derivatives have anticancer effects through the suppression of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Therefore, the synthesized cremastranone derivatives could be applied as novel therapeutic agents against colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Anticancer effect; Apoptosis; Cell cycle; Colorectal cancer; Homoisoflavane derivatives of cremastranone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cremastranone-Derived Homoisoflavanes Suppress the Growth of Breast Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Caspase-Independent Cell Death.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Sep 1;31(5):526-535. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.057. Epub 2023 May 25. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37226044 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum to "Synthetic Homoisoflavane Derivatives of Cremastranone Suppress Growth of Colorectal Cancer Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Induction of Apoptosis" [Biomol. Ther. 30 (2022) 576-584].Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Jan 1;31(1):139. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.005. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 36535633 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reversine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via upregulation of the Fas and DR5 signaling pathways in human colorectal cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2019 May;54(5):1875-1883. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4746. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30864676
-
Biological Activity, Apoptotic Induction and Cell Cycle Arrest of New Hydrazonoyl Halides Derivatives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(9):1141-1149. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190306123658. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30843494
-
Lycorine inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and primarily exerts in vitro cytostatic effects in human colorectal cancer via activating the ROS/p38 and AKT signaling pathways.Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):19. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7970. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649853 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bio-Prospecting of Crude Leaf Extracts from Thirteen Plants of Brazilian Cerrado Biome on Human Glioma Cell Lines.Molecules. 2023 Feb 1;28(3):1394. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031394. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771057 Free PMC article.
-
Cremastranone-Derived Homoisoflavanes Suppress the Growth of Breast Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Caspase-Independent Cell Death.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Sep 1;31(5):526-535. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.057. Epub 2023 May 25. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37226044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basavarajappa H. D., Lee B., Fei X., Lim D., Callaghan B., Mund J. A., Case J., Rajashekhar G., Seo S.-Y., Corson T. W. Synthesis and mechanistic studies of a novel homoisoflavanone inhibitor of endothelial cell growth. PLoS One. 2014;9:e95694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basavarajappa H. D., Lee B., Lee H., Sulaiman R. S., An H., Magaña C., Shadmand M., Vayl A., Rajashekhar G., Kim E. Y., Suh Y. G., Lee K., Seo S. Y., Corson T. W. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel homoisoflavonoids for retinal neovascularization. J. Med. Chem. 2015;58:5015–5027. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00449. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cerquetti L., Sampaoli C., De Salvo M., Bucci B., Argese N., Chimento A., Vottari S., Marchese R., Pezzi V., Toscano V., Stigliano A. C-MYC modulation induces responsiveness to paclitaxel in adrenocortical cancer cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2015;46:2231–2240. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2902. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

