The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases
- PMID: 35934705
- PMCID: PMC9358121
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-022-00770-4
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases
Abstract
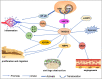
Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) is a member of the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) family. It can promote the formation and rearrangement of disulfide bonds, ensuring proper protein folding. TXNDC5 has three Trx-like domains, which can act independently to introduce disulfide bonds rapidly and disorderly. TXNDC5 is abnormally expressed in various diseases, such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), etc. It can protect cells from oxidative stress, promote cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis and promote the progression of disease. Aberrant expression of TXNDC5 in different diseases suggests its role in disease diagnosis. In addition, targeting TXNDC5 in the treatment of diseases has shown promising application prospects. This article reviews the structure and function of TXNDC5 as well as its role and mechanism in cancer, RA and other diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; Diseases; Rheumatoid arthritis (RA); Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 (TXNDC5).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sullivan DC, Huminiecki L, Moore JW, Boyle JJ, Poulsom R, Creamer D, et al. EndoPDI, a novel protein-disulfide isomerase-like protein that is preferentially expressed in endothelial cells acts as a stress survival factor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(47):47079–47088. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308124200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

