Acylglycerol kinase promotes ovarian cancer progression and regulates mitochondria function by interacting with ribosomal protein L39
- PMID: 35934718
- PMCID: PMC9358817
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02448-5
Acylglycerol kinase promotes ovarian cancer progression and regulates mitochondria function by interacting with ribosomal protein L39
Abstract
Background: Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the leading cause of deaths among patients with gynecologic malignancies. In recent years, cancer stem cells (CSCs) have attracted great attention, which have been regarded as new biomarkers and targets in cancer diagnoses as well as therapies. However, therapeutic failure caused by chemotherapy resistance in late-stage EOC occurs frequently. The 5-year survival rate of patients with EOC remains at about 30%.
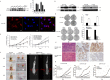
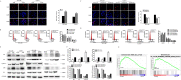
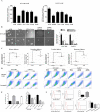
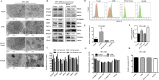
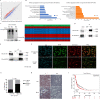
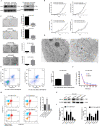
Methods: In this study, the expression of acylglycerol kinase (AGK) was analyzed among patients with EOC. The effect of AGK on EOC cell proliferation and tumorigenicity was studied using Western blotting, flow cytometry, EdU assay and in vivo xenotransplantation assays. Furthermore, AGK induced CSC-like properties and was resistant to cisplatin chemotherapy in the EOC cells, which were investigated through sphere formation assays and the in vivo model of chemoresistance. Finally, the relationship between AGK and RPL39 (Ribosomal protein L39) in mitochondria as well as their effect on the mitochondrial function was analyzed through methods including transmission electron microscopy, microarray, biotin identification and immunoprecipitation.
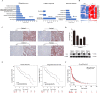
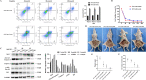
Results: AGK showed a markedly upregulated expression in EOC, which was significantly associated with the poor survival of patients with EOC, the expression of AGK-promoted EOC cell proliferation and tumorigenicity. AGK also induced CSC-like properties in the EOC cells and was resistant to cisplatin chemotherapy. Furthermore, the results indicated that AGK not only maintained mitochondrial cristae morphogenesis, but also increased the production of reactive oxygen species and Δψm of EOC cells in a kinase-independent manner. Finally, our results revealed that AGK played its biological function by directly interacting with RPL39.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that AGK was a novel CSC biomarker for EOC, which the stemness of EOC was promoted and chemotherapy resistance was developed through physical as well as functional interaction with RPL39.
Keywords: Acylglycerol kinase; Epithelial ovarian cancer; Mitochondrial; Ribosomal protein L39; cancer stem cell.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 confers cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells by activating the Notch3 signaling pathway.Int J Cancer. 2019 Oct 1;145(7):1921-1934. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32293. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30895619 Free PMC article.
-
Acylglycerol kinase promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in breast cancer via suppression of the FOXO1 transcription factor.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 8;13:106. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-106. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24886245 Free PMC article.
-
NAMPT Inhibition Suppresses Cancer Stem-like Cells Associated with Therapy-Induced Senescence in Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Res. 2020 Feb 15;80(4):890-900. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2830. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31857293 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on New Hallmarks of Drug-Resistance towards Personalized Care for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Cells. 2024 Mar 31;13(7):611. doi: 10.3390/cells13070611. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of acylglycerol kinase in epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenesis of prostate cancer cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1362-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0331362. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246119 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosomal rodeo: wrangling translational machinery in gynecologic tumors.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec 2;44(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10234-2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 39621173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RPLP2 activates TLR4 in an autocrine manner and promotes HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 5;9(1):440. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01719-0. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38052785 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial medicine: "from bench to bedside" 3PM-guided concept.EPMA J. 2025 Apr 15;16(2):239-264. doi: 10.1007/s13167-025-00409-4. eCollection 2025 Jun. EPMA J. 2025. PMID: 40438494 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Oxidative Phosphorylation-Related Subtypes and Construction of a Prognostic Signature in Ovarian Cancer.Curr Gene Ther. 2025;25(3):327-344. doi: 10.2174/0115665232323373240905104033. Curr Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 39289931
-
MRPL13 enhances mitochondrial function and promotes tumor progression in ovarian cancer by inhibiting mPTP opening via SLC25A6.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Aug 21;16(1):634. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07953-x. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40841355
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZDKJ202003, ZDKJ2021037/Major Science and Technology Program of Hainan Province
- ZDYF2020117/Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund
- 2020TTM008/Tropical Translational Medicine Education Key Laboratory Open Project
- 822MS175/Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province
- 82072880, 82003144, 81660433, 81601317/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

