Unveiling the G4-PAMAM capacity to bind and protect Ang-(1-7) bioactive peptide by molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 35934747
- PMCID: PMC9358120
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-022-00470-5
Unveiling the G4-PAMAM capacity to bind and protect Ang-(1-7) bioactive peptide by molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
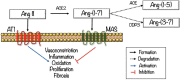
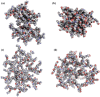
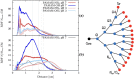
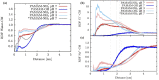
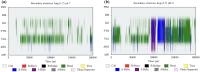
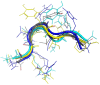
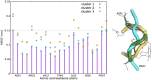
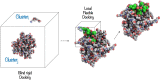
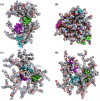
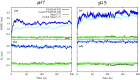
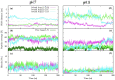
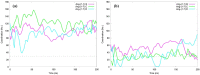
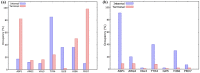
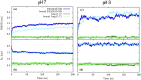
Angiotensin-(1-7) re-balance the Renin-Angiotensin system affected during several pathologies, including the new COVID-19; cardiovascular diseases; and cancer. However, one of the limiting factors for its therapeutic use is its short half-life, which might be overcome with the use of dendrimers as nanoprotectors. In this work, we addressed the following issues: (1) the capacity of our computational protocol to reproduce the experimental structural features of the (hydroxyl/amino)-terminated PAMAM dendrimers as well as the Angiotensin-(1-7) peptide; (2) the coupling of Angiotensin-(1-7) to (hydroxyl/amino)-terminated PAMAM dendrimers in order to gain insight into the structural basis of its molecular binding; (3) the capacity of the dendrimers to protect Angiotensin-(1-7); and (4) the effect of pH changes on the peptide binding and covering. Our Molecular-Dynamics/Metadynamics-based computational protocol well modeled the structural experimental features reported in the literature and our double-docking approach was able to provide reasonable initial structures for stable complexes. At neutral pH, PAMAM dendrimers with both terminal types were able to interact stably with 3 Angiotensin-(1-7) peptides through ASP1, TYR4 and PRO7 key amino acids. In general, they bind on the surface in the case of the hydroxyl-terminated compact dendrimer and in the internal zone in the case of the amino-terminated open dendrimer. At acidic pH, PAMAM dendrimers with both terminal groups are still able to interact with peptides either internalized or in its periphery, however, the number of contacts, the percentage of coverage and the number of hydrogen bonds are lesser than at neutral pH, suggesting a state for peptide release. In summary, amino-terminated PAMAM dendrimer showed slightly better features to bind, load and protect Angiotensin-(1-7) peptides.
Keywords: Ang-(1-7); Dendrimer; G4-PAMAM; Metadynamics; Molecular dynamics; Nanocarrier; PAMAM-OH; Peptide.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The complex of PAMAM-OH dendrimer with Angiotensin (1-7) prevented the disuse-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Mar 13;12:1985-1999. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S125521. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28331320 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic level insights into realistic molecular models of dendrimer-drug complexes through MD simulations.J Chem Phys. 2016 Sep 28;145(12):124902. doi: 10.1063/1.4962582. J Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 27782646
-
Complexation of peptide epitopes with G4-PAMAM dendrimer through ligand diffusion molecular dynamic simulations.J Mol Graph Model. 2020 May;96:107514. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2019.107514. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Mol Graph Model. 2020. PMID: 31877401
-
Dendrimers: Exploring Their Wide Structural Variety and Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Nov 9;15(22):4369. doi: 10.3390/polym15224369. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38006093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shape-Persistent Dendrimers.Molecules. 2023 Jul 20;28(14):5546. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145546. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitigating Cardiotoxicity of Dendrimers: Angiotensin-(1-7) via Its Mas Receptor Ameliorates PAMAM-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction in the Isolated Mammalian Heart.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 1;14(12):2673. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122673. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559167 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Dendrimer-Peptide Therapies for Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 5;15(10):2428. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102428. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muslim S, Nasrin N, Alotaibi FO, Prasad G, Singh SK, Alam I, Mustafa G. Treatment options available for COVID-19 and an analysis on possible role of combination of rhACE2, angiotensin (1–7) and angiotensin (1–9) as effective therapeutic measure. SN Comprehen Clin Med. 2020;2:1761–1766. doi: 10.1007/s42399-020-00407-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

