Recent advances in the study of NADC34-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China
- PMID: 35935186
- PMCID: PMC9354828
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.950402
Recent advances in the study of NADC34-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China
Abstract
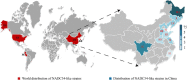
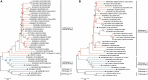
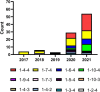
Since porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) was first described in China in 1996, several genetically distinct strains of PRRSV have emerged with varying pathogenicity and severity, thereby making the prevention and control of PRRS more difficult in China and worldwide. Between 2017 and 2021, the detection rate of NADC34-like strain in China increased. To date, NADC34-like strains have spread to 10 Chinese provinces and have thus developed different degrees of pathogenicity and mortality. In this review, we summarize the history of NADC34-like strains in China and clarify the prevalence, genomic characteristics, restriction fragment length polymorphisms, recombination, pathogenicity, and vaccine status of this strain in China. In so doing, this study aims to provide a basis for the further development of prevention and control measures targeting the NADC34-like strain.
Keywords: NADC34-like; PRRSV; RFLP; pathogenicity; recombination.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Wang, Han, Guo, Liu, Hou, Wang, Zheng, Wang and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bassaganya-Riera J., Thacker B. J., Yu S., Strait E., Wannemuehler M. J., Thacker E. L. (2004). Impact of immunizations with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on lymphoproliferative recall responses of CD8+ T cells. Viral. Immunol. 17 25–37. 10.1089/088282404322875430 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

