Phytotoxic effects of Acacia saligna dry leachates on germination, seedling growth, photosynthetic performance, and gene expression of economically important crops
- PMID: 35935250
- PMCID: PMC9354756
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13623
Phytotoxic effects of Acacia saligna dry leachates on germination, seedling growth, photosynthetic performance, and gene expression of economically important crops
Abstract
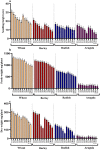
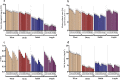
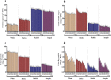
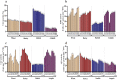
The influence of dry leachates of Acasia saligna was tested on the seedling growth, photosynthesis, biochemical attributes, and gene expression of the economically important crops, including wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), radish (Raphanus sativus L.), barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and arugula (Eruca sativa L.). Different concentrations (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 25%) of stem extract (SE) and leaf extract (LE) of A. saligna were prepared, and seedlings were allowed to grow in Petri plates for 8 days. The results showed that all plant species exhibited reduced germination rate, plant height, and fresh and dry weight due to leachates extracts of A. saligna. Moreover, the activities of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX), exhibited differential regulation due to the extract treatment. The SOD was increased with increasing the concentration of extracts, while CAT and APX activities were decreased with increasing the extract concentrations. In addition, leachate extract treatment decrease chlorophyll content, photosynthesis, PSII activity, and water use efficiency, with evident effects at their higher concentrations. Furthermore, the content of proline, sugars, protein, total phenols, and flavonoids were reduced considerably due to leachates extract treatments. Furthermore, seedlings treated with high concentrations of LE increased the expression of genes. The present results lead to the conclusion that A. saligna contains significant allelochemicals that interfere with the growth and development of the tested crop species and reduced the crops biomass and negatively affected other related parameters. However, further studies are suggested to determine the isolation and purification of the active compounds present in A. saligna extracts.
Keywords: Acacia saligna; Allelopathy; Allelopathy/phytotoxicity; Gene expression; Osmolytes; Secondary metabolism.
© 2022 ALHaithloul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Germination, physiological and biochemical responses of acacia seedlings (Acacia raddiana and Acacia tortilis) to petroleum contaminated soils.Environ Pollut. 2018 Mar;234:642-655. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.067. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Environ Pollut. 2018. PMID: 29223821
-
Differential activity of wheat antioxidant defense system and alterations in the accumulation of osmolytes at different developmental stages as influenced by marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) leachates.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 1;13:1001394. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1001394. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36531349 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of antibiotics stress on root development, seedling growth, antioxidant status and abscisic acid level in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Mar 1;252:114621. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114621. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 36774794
-
Bioactive Phytochemicals of Acacia saligna.Molecules. 2023 May 28;28(11):4396. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114396. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allelopathy and Allelochemicals of Imperata cylindrica as an Invasive Plant Species.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;11(19):2551. doi: 10.3390/plants11192551. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The inhibitory potential of green manure return on the germination and seedling growth of Eleusine indica L.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 7;15:1287379. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1287379. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38384751 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation of Cadmium and Nickel Toxicity and Phyto-Stimulation of Tomato Plant L. by Endophytic Micrococcus luteus and Enterobacter cloacae.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 3;11(15):2018. doi: 10.3390/plants11152018. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956496 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the roots of Hippophae rhamnoides at different stump heights and the root microenvironment in feldspathic sandstone areas.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 27;11:e14819. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14819. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36726726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel Maksoud MIA, Mohamad B, Dina ME, Sofy AR, Sofy MR. Gamma radiation-induced synthesis of a novel chitosan/silver/Mn-Mg ferrite nanocomposite and its impact on cadmium accumulation and translocation in brassica plant growth. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2022;194(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.197. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abou El-Ghit HM. Physiological allelopathic effect of aqueous extracts of cucumber, carrot, onion, and garlic seeds on germination and growth of Pea. Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences. 2016;4:13–19.
-
- Abu-Shahba MS, Mansour MM, Mohamed HI, Sofy MR. Effect of biosorptive removal of cadmium ions from hydroponic solution containing indigenous garlic peel and mercerized garlic peel on lettuce productivity. Scientia Horticulturae. 2022;293(5):110727. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110727. - DOI
-
- Agha MS, Abbas MA, Sofy MR, Haroun SA, Mowafy AM. Dual inoculation of Bradyrhizobium and Enterobacter alleviates the adverse effect of salinity on Glycine max seedling. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca. 2021;49(3):12461. doi: 10.15835/nbha49312461. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

