Advanced oxidation protein products induce annulus fibrosus cell senescence through a NOX4-dependent, MAPK-mediated pathway and accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 35935259
- PMCID: PMC9354796
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13826
Advanced oxidation protein products induce annulus fibrosus cell senescence through a NOX4-dependent, MAPK-mediated pathway and accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration
Abstract
Background: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is closely associated with senescence. Annulus fibrosus (AF) cell senescence is a crucial driver of AF tissue tearing and fissures, thereby exacerbating IVDD. Increased advanced oxidative protein products (AOPPs) were found in human degenerative discs and aged rat discs and may be involved in IVDD. This study aimed to explore the mechanism of AOPPs-induced senescence in AF cells.
Methods: The pathological effects of AOPPs in vivo were investigated using a rat lumbar disc persistent degeneration model and a rat caudal disc puncture model. Rat primary AF cells were selected as in vitro models, and AOPPs were used as direct stimulation to observe their pathological effects. Setanaxb (NOX1/4 inhibitor), apocynin (NADPH oxidase inhibitor) and adenovirus (ADV) packed NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) specific shRNAs were used for pathway inhibition, respectively. Finally, adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) packed with NOX4-specific blocking sequences were used to inhibit the in vivo pathway.
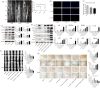
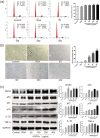
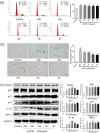
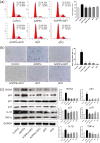
Results: AOPPs accumulated in the rat lumbar and caudal degenerative discs. Intra-discal loading of AOPPs up-regulated the expression of NOX4, p53, p21, p16, IL-1β, and TNF-α, ultimately accelerating IVDD. Exposure of AOPPs to AF primary cells up-regulated NOX4 expression, induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), triggered senescence and increased IL-1β and TNF-α. Apocynin, setanaxib, and ADV pre-cultured AF cells abrogated AOPPs-induced senescence. AAV-mediated inhibition of NOX4 expression in vivo reduced the expression of p53, p21, p16, IL-1β and TNF-α in vivo and delayed IVDD.
Conclusions: AOPPs induced AF cell senescence through a NOX4-dependent and MAPK-mediated pathway.
Keywords: Advanced oxidized protein products; Inflammation associated with senescence; Intervertebral disc degeneration; Senescence.
©2022 Dai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced oxidation protein products increase TNF-α and IL-1β expression in chondrocytes via NADPH oxidase 4 and accelerate cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis progression.Redox Biol. 2020 Jan;28:101306. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101306. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 31539804 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PP2A ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration by reducing annulus fibrosus cells apoptosis via p38/MAPK signal pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Jan;1870(1):166888. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166888. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 37722489
-
Melatonin Inhibits Annulus Fibrosus Cell Senescence through Regulating the ROS/NF-κB Pathway in an Inflammatory Environment.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 18;2021:3456321. doi: 10.1155/2021/3456321. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34458366 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Ferroptosis Holds Potential for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Therapy.Cells. 2022 Nov 5;11(21):3508. doi: 10.3390/cells11213508. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell sequencing: New insights for intervertebral disc degeneration.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115224. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115224. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37516017 Review.
Cited by
-
HIF-1α-induced expression of the m6A reader YTHDF1 inhibits the ferroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by promoting SLC7A11 translation.Aging Cell. 2024 Sep;23(9):e14210. doi: 10.1111/acel.14210. Epub 2024 May 23. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38783692 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal NOX4-Mediated Oxidative Damage Induces Premature Placental Senescence in Obese Pregnancy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Aug 17;18:4705-4726. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S419081. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37608820 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role and therapeutic implications of p53 in intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 1;9(1):433. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01730-5. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38040675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant strategies against cellular senescence: unveiling the power of synthetic versus natural antioxidants in a systematic review.Front Aging. 2025 May 27;6:1543360. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1543360. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40496803 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Senescence in Intervertebral Disc Aging and Degeneration: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Opportunities.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 18;13(4):686. doi: 10.3390/biom13040686. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Weiler C, Paesold G, Jochum M, Boos N. Analysis of tissue distribution of TNF-alpha, TNF-alpha-receptors, and the activating TNF-alpha-converting enzyme suggests activation of the TNF-alpha system in the aging intervertebral disc. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2007;1096:44–54. doi: 10.1196/annals.1397.069. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

