Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in Mixed Dry Eye Disease
- PMID: 35935315
- PMCID: PMC9329033
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1534142
Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in Mixed Dry Eye Disease
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in Mixed Dry Eye Disease.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9830234. doi: 10.1155/2023/9830234. eCollection 2023. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37547649 Free PMC article.
Abstract
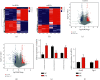
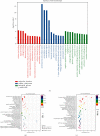
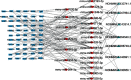
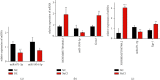
In order to investigate the relationship between inflammation and lncRNA in mixed dry eye disease (DED), this study establishes competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in mixed DED. Microarray analysis of cornea from mixed DED mice is performed to screen for differences in lncRNA and target genes, and miRNA bioinformatics were predicted based on the ceRNA hypothesis. The ceRNA network, which consists of 96 relationship pairs, is constructed using the top 10 upregulated lncRNAs and all upregulated mRNAs and two pairs of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA pairs (NONMMUT047964.2-miR-671-5p-Egr-1andNONMMUT054540.2-miR-1934-5p-Grm2) are selected for RT-qRCR verification in mouse corneal epithelial cells under high osmotic pressure and the samples for microarray. Meanwhile, mouse corneal epithelial cell lines (MCECs), transfected siRNA of NONMMUT047964.2 under high osmotic pressure, shows a decrease in apoptosis rate and a decrease in expression of IL-1β and IL-6. The experimental results show that the NONMMUT047964.2-miR-671-5p-Egr-1 axis may regulate the inflammation and promote the apoptosis of corneal epithelial cells under hypertonic condition.
Copyright © 2022 Zhongxia Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research is conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in human aortic dissection.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 7;22(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08012-3. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34620091 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA network in periodontitis.J Periodontal Res. 2018 Aug;53(4):495-505. doi: 10.1111/jre.12539. Epub 2018 Mar 8. J Periodontal Res. 2018. PMID: 29516510
-
The topological key lncRNA H2k2 from the ceRNA network promotes mesangial cell proliferation in diabetic nephropathy via the miR-449a/b/Trim11/Mek signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):11492-11506. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900522R. Epub 2019 Jul 23. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31336052
-
A ceRNA network of BBOX1-AS1-hsa-miR-125b-5p/hsa-miR-125a-5p-CDKN2A shows prognostic value in cervical cancer.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Mar;60(2):253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2020.12.006. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33678324
-
Long Noncoding RNA 3632454L22Rik Contributes to Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing by Sponging miR-181a-5p in Diabetic Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Nov 1;62(14):16. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.14.16. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34787641 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in Mixed Dry Eye Disease.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9830234. doi: 10.1155/2023/9830234. eCollection 2023. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37547649 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the role of miR-671 in human disorders.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 5;9:1077968. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1077968. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36545507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dong L., Satpute M. N., Wu W., Du D.-Z. Two-phase multidocument summarization through content-attention-based subtopic detection. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems . 2021;8(6):1379–1392. doi: 10.1109/tcss.2021.3079206. - DOI
-
- Chen H., Qiao H., Xu L., Feng Q., Cai K. A fuzzy optimization strategy for the implementation of RBF LSSVR model in vis-NIR analysis of pomelo maturity. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics . 2019;15(11):5971–5979. doi: 10.1109/tii.2019.2933582. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
