Design and Clinical Application Effect Analysis of a New Type of Oral Fluid Suction Device for Patients with Orotracheal Intubation
- PMID: 35935331
- PMCID: PMC9329030
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6057115
Design and Clinical Application Effect Analysis of a New Type of Oral Fluid Suction Device for Patients with Orotracheal Intubation
Abstract
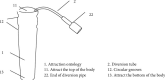
Tracheal intubation is an important access to general anesthesia surgery or respiratory support in critically ill patients. Orotracheal intubation is the most common method of establishing artificial airways in clinical practice. Tracheal intubation and mechanically assisted breathing are among the important steps in the clinical rescue of critically ill patients. During tracheal intubation, it easily causes iatrogenic skin damage, unclear mouth, ulcer, and other oral mucosal complications due to the improper fixation method and excellent dental pads. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to design a novel oral suction device for patients with orotracheal intubation and explore its safety, convenience, and comfort in the clinical application of orotracheal intubation patients. From October 2016 to April 2017, a total of 232 patients with mechanical ventilation through orotracheal intubation in the Department of Surgery and Critical Care Medicine were selected by the convenience sampling method. According to the random number table method, 232 cases were divided into the experimental group and control group, with 116 cases in each group. The experimental group used a self-designed oral fluid suction device to fix the tracheal intubation; the control group used the traditional method, placing ordinary disposable tooth pads, and then using 3M tape to fix the tracheal intubation. The incidence of oral mucosa and lip pressure ulcers, patient comfort, and tracheal tube displacement were observed and compared between the two groups. The incidence of oral mucosa and lip pressure ulcers in the observation group using the self-designed oral fluid suction device to fix the tracheal intubation was significantly lower than that in the control group. At the same time, the comfort of the patients was significantly higher than that of the control group, the incidence of tracheal tube displacement was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the differences between the above indicators were statistically significant (P < 0.05). For patients with orotracheal intubation, using a new oral fluid suction device to fix the tracheal intubation can effectively prevent the displacement of the tracheal intubation, protect the oral mucosa and lips, and reduce the pain of the patient. At the same time, the oral fluid suction device designed in this study has low production cost, strong practicability, and is suitable for clinical promotion.
Copyright © 2022 Yanying Qian and Haifei Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characteristics of oral mucosal pressure injuries in children with orotracheal intubation in intensive care units: An observational study.Nurs Crit Care. 2025 May;30(3):e13174. doi: 10.1111/nicc.13174. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Nurs Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 39349370 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of the effect of a new fixation tape for tracheal catheter in intensive care patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Sep;29(9):836-839. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.09.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28936962 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Evidence-based practice of self-made tracheal catheter fixation band in prevention of unplanned extubation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Mar;34(3):311-314. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211011-01458. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35574752 Chinese.
-
Tracheal suction at birth in non-vigorous neonates born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 16;6(6):CD012671. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012671.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34133025 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of airway colonization in critically ill COPD patient.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Apr;12(4):514-20. doi: 10.2174/138945011794751537. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21194404 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful treatment of endotracheal intubation-related lip pressure injury using a self-developed fixation device.Crit Care. 2023 Jul 24;27(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04577-5. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37488641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protocols and their effects for medical device-related pressure injury prevention among critically ill patients: a systematic review.BMC Nurs. 2024 Jun 17;23(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02080-y. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38886734 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a New Type of Protective Sputum Suction Device in Clinic against Cross-Infection between Medical Staff and Patients.Crit Care Res Pract. 2023 Dec 31;2023:9927819. doi: 10.1155/2023/9927819. eCollection 2023. Crit Care Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 38187985 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a self-developed fixation device on preventing endotracheal intubation-related pressure injury: a randomised controlled trial.Crit Care. 2024 Mar 19;28(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-04874-7. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 38504251 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Li X., Liu J., Ouyang C., Feng J., Kuang M., Yin L. Application of portable fiberoptic bronchoscope-guided nasotracheal intubation in the rescue of patients with respiratory failure[J] Guangdong Medical Journal . 2020;41(6):580–584.
-
- Wang X., Xu X., Zeng Z. Observation on the effect of improved method for preventing oral pressure ulcers in patients with oral tracheal intubation[J] Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine . 2011;30(7):31–32.
-
- Mi Y., Cheng M., Yuan X. Design and application of dental pad protective cover for orotracheal intubation [J] China Clinical Nursing . 2015;7(2):185–186.
-
- Kong J. Analysis of the causes and countermeasures of oral and cervical pressure ulcers in patients with endotracheal intubation [J] Chinese Nursing Research . 2013;27(5B):1360–1361.
-
- Li Y. Application of syringe in fixation of orotracheal intubation [J] Chinese Critical Care Medicine . 2009;2l(11):p. 651.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous