Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Key Signal Pathways Affecting the Prognosis of Glioma
- PMID: 35935338
- PMCID: PMC9354928
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.910543
Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Key Signal Pathways Affecting the Prognosis of Glioma
Abstract
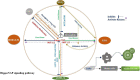
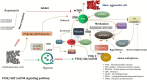
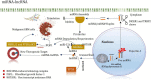
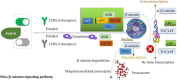
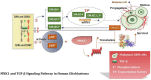
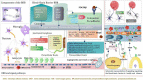
As is known to all, glioma, a global difficult problem, has a high malignant degree, high recurrence rate and poor prognosis. We analyzed and summarized signal pathway of the Hippo/YAP, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, miRNA, WNT/β-catenin, Notch, Hedgehog, TGF-β, TCS/mTORC1 signal pathway, JAK/STAT signal pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, the relationship between BBB and signal pathways and the mechanism of key enzymes in glioma. It is concluded that Yap1 inhibitor may become an effective target for the treatment of glioma in the near future through efforts of generation after generation. Inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Shh, Wnt/β-Catenin, and HIF-1α can reduce the migration ability and drug resistance of tumor cells to improve the prognosis of glioma. The analysis shows that Notch1 and Sox2 have a positive feedback regulation mechanism, and Notch4 predicts the malignant degree of glioma. In this way, notch cannot only be treated for glioma stem cells in clinic, but also be used as an evaluation index to evaluate the prognosis, and provide an exploratory attempt for the direction of glioma treatment. MiRNA plays an important role in diagnosis, and in the treatment of glioma, VPS25, KCNQ1OT1, KB-1460A1.5, and CKAP4 are promising prognostic indicators and a potential therapeutic targets for glioma, meanwhile, Rheb is also a potent activator of Signaling cross-talk etc. It is believed that these studies will help us to have a deeper understanding of glioma, so that we will find new and better treatment schemes to gradually conquer the problem of glioma.
Keywords: gene expression; glioma; neoplastic; prognosis; signal pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Wei, Li, Ma and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between PI3K/AKT/mTOR and WNT/β-Catenin signaling in GBM - Could combination therapy checkmate the collusion?Cell Signal. 2022 Jul;95:110350. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110350. Epub 2022 May 4. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35525406 Review.
-
LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and predicts poor survival of glioma patients.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 12;37(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30208924 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-451 Inhibits Glioma Cell Proliferation and Invasion Through the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway by Targeting CAB39.Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev. 2018 Sep;29(3):156-166. doi: 10.1089/humc.2018.133. Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev. 2018. PMID: 30180756
-
Long noncoding RNA KB-1460A1.5 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis via miR-130a-3p/TSC1/mTOR/YY1 feedback loop.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jan 28;525:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.033. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 34728310
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jan 26;29(1):71-91. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28822229 Review.
Cited by
-
Glioma Stem Cells-Features for New Therapy Design.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;16(8):1557. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081557. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ODF3B affects the proliferation and apoptosis of glioma via the JAK/STAT pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 15;14(3):1419-1432. doi: 10.62347/GHKF1995. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38590411 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 Promotes Glioma Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration via Mir-142-3p/KCNQ1OT1/HMGB3 Axis : Running Title: EZH2 Promotes Glioma cell Malignant Behaviors.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):8668-8687. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04080-0. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38556567
-
LncRNA NDUFA6-DT: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Potential LncRNA Biomarker and Its Regulatory Mechanisms in Gliomas.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;15(4):483. doi: 10.3390/genes15040483. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674418 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Image-Based Models for High-Grade Gliomas Might Be Accelerated.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;16(8):1566. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081566. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

