Hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndrome-Clinical insights from a large longitudinal cohort in a single medical center
- PMID: 35935360
- PMCID: PMC9352926
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.916679
Hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndrome-Clinical insights from a large longitudinal cohort in a single medical center
Abstract
Background: Hypoparathyroidism, retardation, and dysmorphism (HRD) Syndrome is a rare disease composed of hypoparathyroidism, retardation of both growth and development, and distinctive dysmorphic features. Here, we describe the long-term morbidity and mortality in a large cohort of HRD patients and suggest recommendations for follow up and treatment.
Methods: Medical records of 63 HRD syndrome patients who were followed at Soroka Medical Center during 1989-2019 were reviewed retrospectively. Information regarding demographics, medical complications, laboratory findings, and imaging studies was collected.
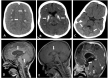
Results: The mortality rate was 52%. The main causes of death were infectious diseases including pneumonia, septic shock, and meningitis. Multiple comorbidities were found including brain anomalies in 90% of examined patients (basal ganglia calcifications, tightening of corpus callosum, Chiari malformation, hydrocephalous, and brain atrophy), seizures in 62%, nephrocalcinosis and/or nephrolithiasis in 47%, multiple eye anomalies were recorded in 40%, bowel obstructions in 9.5%, and variable expression of both conductive and senso-neural hearing loss was documented in 9.5%.
Conclusion: HRD is a severe multisystem disease. Active surveillance is indicated to prevent and treat complications associated with this rare syndrome.
Keywords: HRD; Sanjad-Sakati; bowel obstruction; infections; nephrolithiasis; seizures.
Copyright © 2022 David, Agur, Novoa, Shaki, Walker, Carmon, Eskin-Schwartz, Birk, Ling, Schreiber, Loewenthal, Haim and Hershkovitz.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

