The Utility of Peripheral Blood Leucocyte Ratios as Biomarkers in Neonatal Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35935369
- PMCID: PMC9353072
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.908362
The Utility of Peripheral Blood Leucocyte Ratios as Biomarkers in Neonatal Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Early stage diagnosis of neonatal sepsis (NS) remains a major roadblock due to non-specific symptoms and the absence of precise laboratory index tests. The full blood count is a relatively cheap, universal, and rapid diagnostic test.
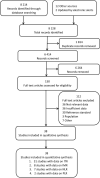
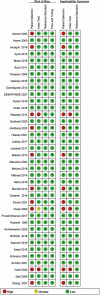
Method: This study assessed the diagnostic accuracies of immature-to-total neutrophil ratio (ITR), immature-to-mature neutrophil ratio (IMR), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) used in the diagnosis of NS. Included studies were retrieved by searching four major databases and relevant references, and reviewed based on the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Pooled sensitivities and specificities were calculated, I 2 was utilized to test for heterogeneity, and the source was investigated via meta-regression analysis.
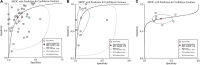
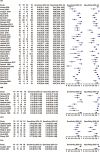
Results: Finally, 38 studies passed the eligibility criteria. A total of thirty-one studies (6,221 neonates) included data on the ITR, eight studies (1,230 neonates) included data on the IMR, seven studies (751 neonates) included data on the NLR, and two studies (283 neonates) included data on the PLR. The summary sensitivity estimates with 95% confidence interval (CI) for the ITR, IMR, NLR, and PLR tests were, respectively, 0.74 (95% CI: 0.66-0.80), 0.74 (95% CI: 0.54-0.88), 0.73 (95% CI: 0.68-0.78), and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.55-1.00). The summary specificity values for the ITR, IMR, NLR, and PLR tests were 0.83 (95% CI: 0.77-0.87), 0.89 (95% CI: 0.80-0.94), 0.69 (95% CI: 0.57-0.79), and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.81-1.00), respectively. The area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curves for the ITR, IMR, and NLR tests were 0.85 (95% CI: 0.82-0.88), 0.91 (95% CI: 0.88-0.93), and 0.75 (95% CI: 0.71-0.79). The PLR could not be evaluated because only two studies included pertinent data.
Conclusion: The NLR test might not be sufficiently accurate in precisely diagnosing NS. The ITR and IMR tests alone can improve the accuracy of NS diagnosis, but the marked heterogeneity and the limited number of studies prevented us from reaching any definitive conclusions. Thus, further studies are warranted to validate these findings.
Systematic review registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42021247850].
Keywords: immature-to-mature neutrophil ratio; immature-to-total neutrophil ratio; meta-analysis; neonatal sepsis; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zeng, Zhang, Yu, Guo and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy of complete blood cell count and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, lymphocyte-to-monocyte, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios for neonatal infection.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2022 Feb 28;16(1):43-52. doi: 10.2478/abm-2022-0006. eCollection 2022 Feb. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2022. PMID: 37551395 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in diagnosing neonatal sepsis.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e763. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.763. Epub 2024 May 31. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280270 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic predictive values of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-1 expression in neonatal sepsis: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jul 22;10:929665. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.929665. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35935355 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Jun 30;23(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04094-y. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37391699 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the prognosis and risk of death for adult sepsis patients: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1336456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336456. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38562922 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A meta-analysis on first-trimester blood count parameters-is the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio a potentially novel method for first-trimester preeclampsia screening?Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 3;11:1336764. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1336764. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38633299 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Potentially Fatal COVID-19 Disease in Pregnant Patients Using the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR).J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 2;12(21):6896. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216896. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959361 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Role of NLR, dNLR, PLR, NLPR, and Other Laboratory Markers in Diagnosing SIRS in Premature Newborns.Clin Pract. 2024 Jun 6;14(3):1065-1075. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14030084. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38921262 Free PMC article.
-
[Prognostic utility of inflammatory indexes in critically ill newborns].Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023 Sep 18;61(Suppl 2):S171-S177. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023. PMID: 38011646 Free PMC article. Spanish.
References
-
- Ognean ML, Boicean A, Sular F, Cucerea M. Complete blood count and differential in diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis. Rev Rom Med Lab. (2017) 25:101–8. 10.1515/rrlm-2016-0042 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

