Congenital etiologies of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- PMID: 35935370
- PMCID: PMC9354839
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.909925
Congenital etiologies of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Abstract
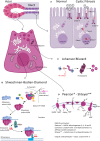
Congenital exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a rare condition. In a vast majority of patients, exocrine dysfunction occurs as part of a multisystemic disease, the most prevalent being cystic fibrosis and Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome. Recent fundamental studies have increased our understanding of the pathophysiology of these diseases. Exocrine pancreatic dysfunction should be considered in children with failure to thrive and fatty stools. Treatment is mainly supportive and consists of pancreatic enzyme replacement and liposoluble vitamins supplementation.
Keywords: Johanson-Blizzard syndrome; Pearson syndrome; Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome; cystic fibrosis; exocrine pancreatic insufficiency; pancreas agenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Scheers and Berardis.
Conflict of interest statement
IS was supported by a Grant Fondation Contre le Cancer (FCC-Post Doctoral funding; #2017-036), Fondation Saint-Luc for Cancer, Fondation Saint-Luc Unlock for Lives, and Fonds National pour la Recherche Scientifique (FNRS-CDR; #J.0161.21). The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Delachaume-Salem E, Sarles H. Normal human pancreatic secretion in relation to age. Biol Gastroenterol. (1970) 2:135–46. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

