Analytical performances of different diagnostic methods for SARS-CoV-2 virus - A review
- PMID: 35935464
- PMCID: PMC9338831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sintl.2022.100197
Analytical performances of different diagnostic methods for SARS-CoV-2 virus - A review
Abstract
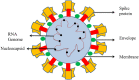
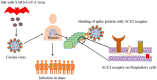
Covid-19 is a dreadful pandemic of the 21st century that has created fear among people, affected the whole world, and taken thousands of lives. It infects the respiratory system and causes flu-type symptoms. According to the WHO reports, 2,082,745 deaths and 96,267,473 confirmed cases were perceived all around the globe till January 22, 2021. The significant roots of transmission are inhalation and direct contact with the infected surface. Its incubation period is 2-14 days and remains asymptomatic in most people. However, no treatment and vaccine are available for the people, so preventive measures like social distancing, wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), and frequent hand-washing are the practical and only options for cure. It has affected every sector of the world, whether it is trade or health all around the world. There is high demand for diagnostic tools as high-scale and expeditious testing is crucial for controlling disease spread; thus, detection methods play an essential role. Like flu, Covid-19 is also detected through RT-PCR, as the World Health Organization (WHO) suggested, but it is time taking and expensive method that many countries cannot afford. A vaccine is a crucial aspect of eradicating disease, and for SARS-CoV-2), plasma therapy and antibiotics therapy are used in the early spreading phase. The later stage involves forming a vaccine based on spike protein, N-protein, and whole-viral antigen that effectively immunizes the population worldwide until herd immunity can be achieved. In this review, we will discuss all possible and developed techniques for identifying SARS-CoV-2 and make a comparison of their specificity, selectivity, and cost; thus, we choose an appropriate method for fast, reliable, and pocket-friendly detection.
Keywords: Biosensor; Covid-19; Lateral flow immunoassay; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The British variant of the new coronavirus-19 (Sars-Cov-2) should not create a vaccine problem.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021 Jan-Feb;35(1):1-4. doi: 10.23812/21-3-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021. PMID: 33377359
-
Comparative evaluation of RT-PCR and antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) for SARS-CoV-2 detection: performance, variant specificity, and clinical implications.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0007324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00073-24. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38683014 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;222(6):521-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32217113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Evaluation of the Rapid Antigen Detection Kit with the Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Samples].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022 Apr;56(2):263-273. doi: 10.5578/mb.20229806. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022. PMID: 35477229 Turkish.
Cited by
-
Detection of Specific RNA Targets by Multimerization.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023 May;88(5):679-686. doi: 10.1134/S0006297923050103. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023. PMID: 37331713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Aleem A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19) Statpearls. 2022 [internet] - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Zhang W., Lu Y., Guo C., Guo Z., Liao C., Zhang X., Zhang Y., Han X., Li Q., Lipkin W.I. BioRxiv; 2020. From SARS-CoV to Wuhan 2019-nCoV Outbreak: Similarity of Early Epidemic and Prediction of Future Trends.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
