Development of in situ bioprinting: A mini review
- PMID: 35935512
- PMCID: PMC9355423
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.940896
Development of in situ bioprinting: A mini review
Abstract
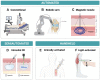
Bioprinting has rapidly progressed over the past decade. One branch of bioprinting known as in situ bioprinting has benefitted considerably from innovations in biofabrication. Unlike ex situ bioprinting, in situ bioprinting allows for biomaterials to be printed directly into or onto the target tissue/organ, eliminating the need to transfer pre-made three-dimensional constructs. In this mini-review, recent progress on in situ bioprinting, including bioink composition, in situ crosslinking strategies, and bioprinter functionality are examined. Future directions of in situ bioprinting are also discussed including the use of minimally invasive bioprinters to print tissues within the body.
Keywords: bedside mounted bioprinter; bioink; crosslinking; handheld bioprinter; in situ bioprinting; minimally invasive.
Copyright © 2022 MacAdam, Chaudry, McTiernan, Cortes, Suuronen and Alarcon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal S., Saha S., Balla V. K., Pal A., Barui A., Bodhak S. (2020). Current developments in 3D bioprinting for tissue and organ regeneration–A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 6. 10.3389/fmech.2020.589171 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

