A Novel Identified Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA, LINC01574, Contributes to Breast Cancer Deterioration via the Regulation of miR-6745/TTYH3 Axis
- PMID: 35935583
- PMCID: PMC9348968
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4201283
A Novel Identified Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA, LINC01574, Contributes to Breast Cancer Deterioration via the Regulation of miR-6745/TTYH3 Axis
Abstract
Objective: Compelling evidence suggested that lncRNAs performed vital functions in the development of breast cancer (BC). The study intended to mine the functional roles of LINC01574 in BC and further excavated its underlying regulatory mechanism.
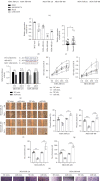
Methods: The expression and prognosis of LINC01574 in BC were detected by integrating analysis of data mining, bioinformatics, and RT-qPCR. Then, the effect of LINC01574 knockdown on BC cell growth and metastasis was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Interactions between miR-6745 and LINC01574 or TTYH3 were revealed by both target prediction and dual luciferase reporter assay.
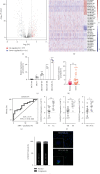
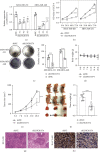
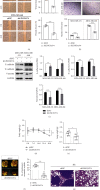
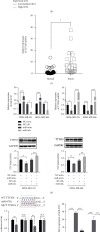
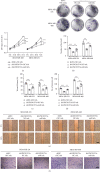
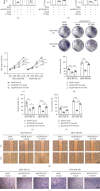
Results: Our data found that LINC01574 was markedly elevated in BC tissues and cells and was an independent prognostic risk factor for patients with BC. Further functional studies revealed that knockdown of LINC01574 remarkably inhibited the growth and metastasis of BC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, LINC01574 competitively binds with miR-6745 to prevent the degradation of TTYH3, thereby promoting the development of BC.
Conclusion: Our results unmasked a novel LINC01574/miR-6745/TTYH3 regulatory axis in BC progression and suggested that LINC01574 might be a promising prognostic indicator and therapeutic target for patients with BC.
Copyright © 2022 Liang Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mathew A., George P. S., Arjunan A., et al. Temporal trends and future prediction of breast cancer incidence across age groups in Trivandrum, South India. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention : APJCP . 2016;17(6):2895–2899. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

