Case report: Changes in the levels of stress hormones during Takotsubo syndrome
- PMID: 35935637
- PMCID: PMC9354975
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.931054
Case report: Changes in the levels of stress hormones during Takotsubo syndrome
Abstract
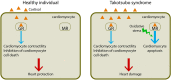
Background: Takotsubo syndrome is an acute cardiac condition usually involving abnormal regional left ventricular wall motion and impaired left ventricular contractility. It is due mainly to hyper-stimulation of the sympathetic nerve system, inducing an excess of catecholamines, usually triggered by intense psychological or physiological stress. The relationship between Takotsubo syndrome and the circulating stress hormones cortisol and copeptin (a surrogate marker of arginine vasopressin) has not been well documented.
Case summary: Here, we describe the dynamic changes in circulating cortisol and copeptin during an entire episode of Takotsubo syndrome in a post-partum woman after spontaneous vaginal delivery. The patient was diagnosed with inverted Takotsubo syndrome accompanied by HELLP syndrome. We found qualitative and quantitative changes in cortisol: a loss of circadian rhythm and a three-fold elevation in the plasma concentration of the hormone with a peak appearing several hours before circulating cardiac biomarkers began to rise. By contrast, levels of copeptin remained normal during the entire episode.
Discussion: Our findings indicate that the levels of cortisol change during Takotsubo syndrome whereas those of copeptin do not. This association between elevated cortisol and Takotsubo syndrome suggests that aberrant levels of this stress hormone may contribute to the observed cardiac pathology. We conclude that biochemical assays of circulating cortisol and cardiac biomarkers may be a useful complement to the diagnosis of Takotsubo syndrome by non-invasive cardiac imaging.
Keywords: Takotsubo syndrome; cardiac biomarkers; case report; copeptin; cortisol.
Copyright © 2022 Ruiz, Gabarre, Chenevier-Gobeaux, François, Kerneis, Cidlowski, Oakley, Lefèvre and Boissan.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

