Patency and adverse outcomes of sequential vs. individual saphenous vein grafts in coronary artery bypass: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 35935658
- PMCID: PMC9355302
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.944717
Patency and adverse outcomes of sequential vs. individual saphenous vein grafts in coronary artery bypass: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To undertake a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies to compare the patency and adverse outcomes of sequential and individual saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) in coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
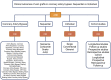
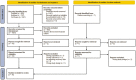
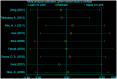
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for cohort studies. Endpoints for vein graft failure, perioperative and follow-up adverse events were extracted as risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). Statistical heterogeneity across the studies was examined using the I2 statistic. Potential of publication bias was evaluated quantitatively by the Egger's test. Sensitivity analysis was also performed to assess the robustness of our outcomes.
Results: The 15 studies were analyzed, including 22,004 patients, 4,580 grafts, and seven different adverse events under individual or sequential CABG. The sequential group had inferior graft failure (RR = 0.68; 95% CI, 0.60-0.77) and long-term mortality (RR = 0.76; 95%CI, 0.61-0.95), but with an increased risk of perioperative repeat revascularization (RR = 1.58; 95%CI, 1.16-2.14) than the individual group.
Conclusion: Taken together, our analysis of the aggregated evidence comparing the sequential and individual saphenous vein grafts for coronary heart disease patients showed that the use of the sequential graft was associated with inferior graft failure and long-term mortality respectively, but with an increased risk of perioperative repeat revascularization. According to our study, both surgical techniques have their own advantages in efficacy and safety, and the selection of surgical techniques should be based on patients and surgeons. Sequential saphenous vein grafts should be more recommended to experienced surgeons in order to both reduce perioperative adverse events and improve long-term patency.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42022326992.
Keywords: all-cause mortality; coronary artery bypass graft; graft failure; individual; revascularization; sequential.
Copyright © 2022 Jiao, Li, Bai and Guo.
Figures
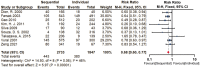

References
-
- World Health Organization . The Top 10 Causes of Death. (2019). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed December 9, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

