The monomeric C-reactive protein level is associated with the increase in carotid plaque number in patients with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35935662
- PMCID: PMC9353581
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.968267
The monomeric C-reactive protein level is associated with the increase in carotid plaque number in patients with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis
Abstract
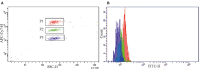
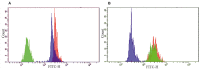
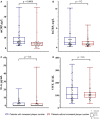
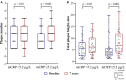
The high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) assay measures the level of the pentameric form of CRP in blood. Currently, there are no available assays measuring the level of the monomeric form of CRP (mCRP), produced at sites of local inflammation. We developed an assay measuring the mCRP level in blood plasma with functional beads for flow cytometry. The assay was used to measure the mCRP level in 80 middle-aged individuals with initially moderate cardiovascular SCORE risk. By the time of the mCRP measurement, the patients have been followed up for subclinical carotid atherosclerosis progression for 7 years. Ultrasound markers of subclinical atherosclerosis, which included plaque number (PN) and total plaque height (PH), were measured at baseline and at the 7th-year follow-up survey. Inflammatory biomarkers, including mCRP, hsCRP, inteleukin-6 (IL-6) and von Willebrand factor (VWF) level, were measured at the 7th-year follow-up survey. The median level of mCRP was 5.2 (3.3; 7.1) μg/L, hsCRP 1.05 (0.7; 2.1) mg/L, IL-6 0.0 (0.0; 2.8) pg/mL, VWF 106 (77; 151) IU/dL. In the patients with the mCRP level below median vs. the patients with the median mCRP level or higher, change from baseline in PN was 0.0 (0.0; 1.0) vs. 1.0 (1.0; 2.0) and PH 0.22 (-0.24; 1.91) mm vs. 1.97 (1.14; 3.14) mm, respectively (p < 0.05). The adjusted odds ratio for the formation of new carotid atherosclerotic plaques was 4.7 (95% CI 1.7; 13.2) for the patients with the median mCRP level or higher. The higher mCRP level is associated with the more pronounced increase in PN and PH in patients with normal level of traditional inflammatory biomarkers and initially moderate cardiovascular SCORE risk.
Keywords: carotid atherosclerosis; hsCRP; inflammatory biomarkers; monomeric C-reactive protein (mCRP); plaque height; plaque number; residual inflammatory risk.
Copyright © 2022 Melnikov, Kozlov, Pogorelova, Tripoten, Khamchieva, Saburova, Avtaeva, Zvereva, Matroze, Kuznetsova, Prokofieva, Balakhonova and Gabbasov.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monomeric form of C-reactive protein in the assessment of the residual inflammatory cardiovascular risk in patients with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis.Kardiologiia. 2022 Jul 31;62(7):24-30. doi: 10.18087/cardio.2022.7.n2137. Kardiologiia. 2022. PMID: 35989626 English, Russian.
-
Higher monomeric C-reactive protein levels are associated with premature coronary artery disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 10;15:1501125. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501125. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39867895 Free PMC article.
-
Monomeric C-Reactive Protein in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Advances and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2079. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032079. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Levels of Endothelial Microparticles Bearing Monomeric C-reactive Protein are Increased in Peripheral Artery Disease.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016 Jun;9(3):184-193. doi: 10.1007/s12265-016-9678-0. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 26891844 Free PMC article.
-
Current Position on the Role of Monomeric C-reactive Protein in Vascular Pathology and Atherothrombosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(1):37-43. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191216144055. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 31840602 Review.
Cited by
-
C-reactive protein conformations and their association with the IL-1β/IL-6 pathway in ocular inflammatory conditions.Front Immunol. 2025 May 12;16:1601145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1601145. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40421028 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of C-reactive protein omics-measures associates methylation risk score with sleep health and related health outcomes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:2024.09.04.24313008. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.24313008. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 May 28;8(1):821. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08226-1. PMID: 39281736 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
C-reactive Protein: An Inflammatory Biomarker and a Predictor of Neurodegenerative Disease in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease?Cureus. 2024 Apr 25;16(4):e59009. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59009. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38665135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mCRP-Induced Focal Adhesion Kinase-Dependent Monocyte Aggregation and M1 Polarization, Which Was Partially Blocked by the C10M Inhibitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 7;25(6):3097. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063097. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542070 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation risk score of C-reactive protein associates sleep health with related health outcomes.Commun Biol. 2025 May 28;8(1):821. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08226-1. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40437222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borén J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, Packard CJ, Bentzon JF, Binder CJ, et al. . Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:2313–30. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. . 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. (2019) 73:e285–350. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

