CoviDetNet: A new COVID-19 diagnostic system based on deep features of chest x-ray
- PMID: 35935665
- PMCID: PMC9347592
- DOI: 10.1002/ima.22771
CoviDetNet: A new COVID-19 diagnostic system based on deep features of chest x-ray
Abstract
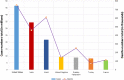
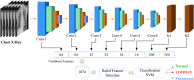
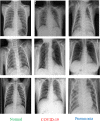
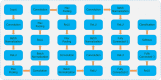
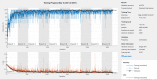
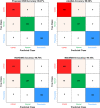
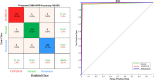
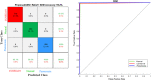
COVID-19 has emerged as a global pandemic affecting the world, and its adverse effects on society still continue. So far, about 243.57 million people have been diagnosed with COVID-19, of which about 4.94 million have died. In this study, a new model, called COVIDetNet, is proposed for automated COVID-19 detection. A lightweight CNN architecture trained instead of the popular and pretrained convolution neural network (CNN) models such as VGG16, VGG19, AlexNet, ResNet50, ResNet100, and MobileNetV2 from scratch with chest x-ray (CXR) images was designed. A new feature set was created by concatenating the features of all layers of the designed CNN architecture. Then, the most efficient features chosen among the features concatenating with the Relief feature selection algorithm were classified using the support vector machine (SVM) method. The experimental works were carried out on a public COVID-19 CXR database. Experimental results demonstrated 99.24% accuracy, 99.60% specificity, 99.39% sensitivity, 99.04% precision, and an F1 score of 99.21%. Also, in comparison to AlexNet and VGG16 models, the deep feature extraction durations were reduced by approximately 6-fold and 38-fold, respectively. The COVIDetNet model provided a higher accuracy score than state-of-the-art models when compared to multi-class research studies. Overall, the proposed model will be beneficial for specialist medical staff to detect COVID-19 cases, as it provides faster and higher accuracy than existing CXR-based approaches.
Keywords: COVID‐19; Relief; SVM; automatic detection; deep feature extraction with a lightweight CNN.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO coronavirus (COVID‐19) dashboard 2020. Accessed December 30, 2021. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Nowrin A, Afroz S, Rahman MS, Mahmud I, Cho YZ. Comprehensive review on facemask detection techniques in the context of Covid‐19. IEEE Access. 2021;9:106839‐106864.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
