Association Between NPHS2 p.R229Q and Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis/Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 35935761
- PMCID: PMC9354893
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.937122
Association Between NPHS2 p.R229Q and Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis/Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
Aim: NPHS2 is the coding gene of podocin. This study aims to investigate the association between NPHS2 p.R229Q (rs61747728), the most frequently reported missense variant of NPHS2, and focal segmental glomerular sclerosis (FSGS) or steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) based on typing the variant in a Chinese FSGS/SRNS cohort and conducting a meta-analysis.
Method: We recruited patients with FSGS or SRNS and healthy individuals. To conduct a meta-analysis, all studies on p.R229Q and FSGS/SRNS were searched from public databases.
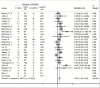
Results: In total, we enrolled 204 patients with FSGS, 61 patients with SRNS [46 with FSGS, 9 with minimal change disease (MCD), and six patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN)], and 100 healthy controls. Unexpectedly, p.R229Q was absent in the patients from our cohort. By meta-analysis of 21 studies including 2,489 patients with FSGS/SRNS and 6,004 healthy controls, we confirmed that the A allele of p.R229Q was significantly associated with increased risk of FSGS/SRNS (allelic OR = 1.9, 95% CI = 1.44-2.52, P < 0.001). However, the subgroup analysis showed that the association between p.R229Q and FSGS/SRNS was true only in Caucasians (allelic OR = 2.14, 95%CI = 1.54-2.98, P < 0.001) and in early-onset patients (allelic OR: 2.13, 95% CI = 1.21-3.76, P = 0.009).
Conclusion: NPHS2 p.R229Q may play an important role in enhancing the susceptibility of FSGS/SRNS, especially in ethnicity of Caucasian and age of early-onset patients.
Keywords: NPHS2; focal segmental glomerular sclerosis; meta-analysis; p.R229Q; steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Weng, Zhang, Liu, Tong, Hao, Shi, Shen, Ren, Xie and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer FL declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors JX, QW, JT, XH, HS, XZ, YL, PS, HR, and NC to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

